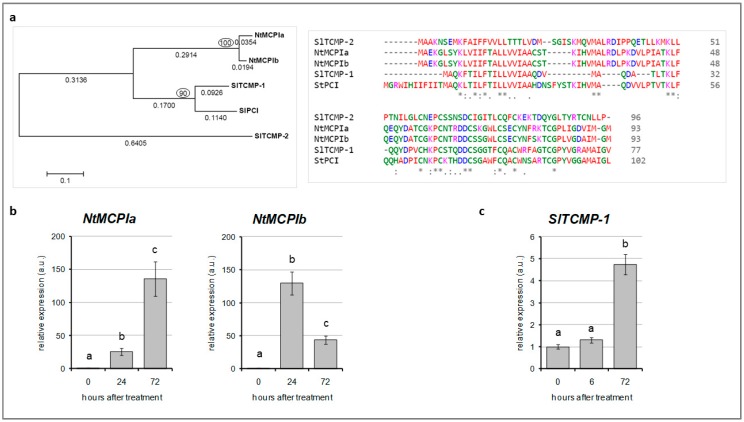
Figure 1.
(a) Left, evolutionary relationships and protein sequence alignment of 5 well characterized metallocarboxypeptidase inhibitors of Nicotiana tabacum (NtMCPIa and NtMCPIb), Solanum tuberosum (StPCI), and Solanum lycopersicum (SlTCMP-1 and SlTCMP-2). The evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method [27]. The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 1.67701287 is shown. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (100 replicates) is shown next to the branches (values circled). The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths (below the branches) in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method [28] and are in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. The analysis involved 5 amino acid sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 75 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA5 [29]. Right, CLUSTAL Omega multiple sequence alignment of the 5 selected proteins [30]. The consensus symbols: “*” identical residues; “:” residues with strongly similar properties; “.” residues with weakly similar properties. (b) NtMCPIa and NtMCPIb mRNA levels in leaves of Nicotiana tabacum plants treated with 10 µM CdSO4 and collected after 6 and 72 h. (c) SlTCMP-1 expression in leaves collected from tomato plants after 6 and 72 h of treatment with 10 µM CdSO4. The values reported in (b,c) are means ± SE of 3 replicates.