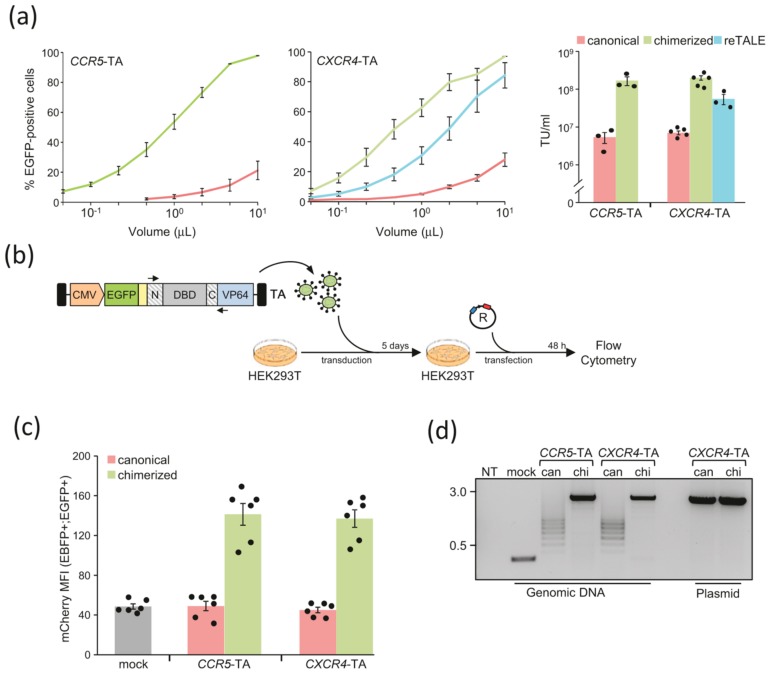
Figure 2.
Lentiviral delivery of chimeric TAs: (a) Titration of lentiviral vectors expressing canonical, chimerized, or recoded TAs (reTALE). Increasing amounts of lentiviral vectors expressing either canonical (light red), chimerized (light green), or recoded (light blue) TAs targeting CCR5 or CXCR4 genes, respectively, were used to transduce HEK293T cells. The extent of EGFP positive cells was measured by flow cytometry and used to determine the viral titer as transducing unit (TU)/mL (right; mean ± SEM). Each dot represents a single data point. (b) Experimental design. HEK293T cells are transduced with the lentiviral vectors containing the indicated CCR5- or the CXCR4-specific TAs. Five days later, transduced cells are transfected with the reporter plasmid (R), described in Figure 1d, and mCherry expression levels measured via flow cytometry two days later are used to estimate TA activity. (c) Activity of TAs. The graph indicates the extent of mCherry expression (mean ± SEM), measured as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI), in the fraction of cells that received the reporter plasmid (EBFP+) and stably express the TA as a consequence of lentiviral vector integration (EGFP+). Basal mCherry expression levels are measured by using a lentiviral vector containing an effector lacking the DNA binding domain (mock, grey bar). Each dot represents a single data point. (d) Analysis of TAs integrity. Seven days post transduction, cells were harvested, and genomic DNA was purified to assess the integrity of the TA expressed from integrated vectors. The integrity of the DNA binding domain (DBD) included in the respective TA is assessed via PCR amplification using the primers depicted in panel b (black arrows). As a positive control, the same PCR is performed on the corresponding plasmid DNA to visualize the size of the amplicon derived from a full-length DBD. DNA marker (in kbp) is indicated on the left.