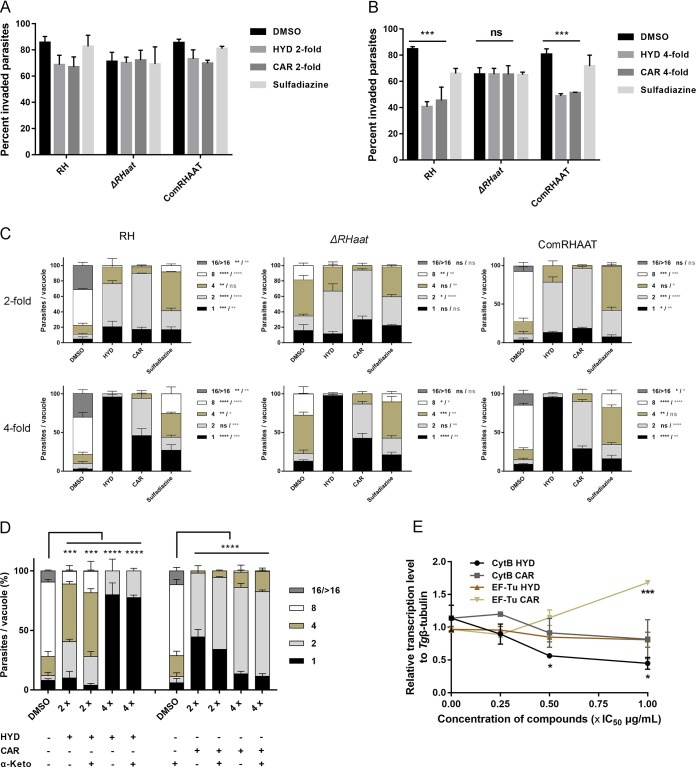
FIG 8.
HYD and CAR inhibit T. gondii growth through an AAT-independent pathway. (A and B) Effects of AAT-deficient parasite invasion treated with HYD and CAR compared to parental and complemented. The data show the means ± the SEM of three independent experiments. ***, P < 0.001, determined by chi-square test. (C) Effects of HYD and CAR treatment for AAT-deficient parasite replication. The concentration of the 2- or 4-fold IC50 values of HYD and CAR were used to treat parasite replication by three strains. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. A heavy asterisk stands for HYD versus vehicle, and a light asterisk stands for CAR versus vehicle, determined by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. (D) α-Ketoglutarate (α-Keto) assay. α-Ketoglutarate was supplemented to the HYD and CAR treatment medium, and then replication was determined at 24 h postinfection. ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001, determined by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. (E) Effects of HYD and CAR on mitochondrial genome and apicoplast genome. A total of 2 × 107 tachyzoites were treated by 0.25-, 0.5-, and 1-fold IC50 values of HYD, CAR, or sulfadiazine (1 mg/ml) for 5 days to investigate the expression of CytB and the EF-Tu gene by qPCR. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA plus Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test.