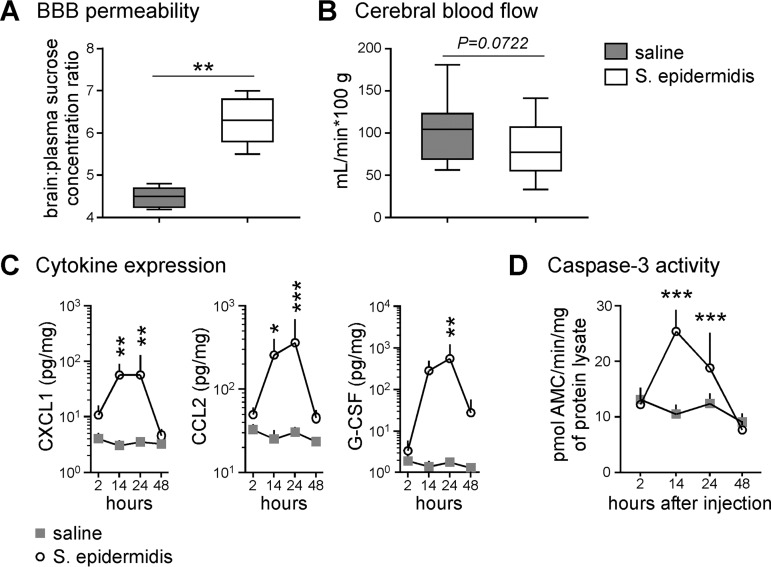
FIG 7.
Perturbations in the brain after systemic S. epidermidis infection. (A) Blood-brain barrier permeability assay. [14C]sucrose was administered to mice 14 hours after S. epidermidis or saline injection (n = 5 per group). Plasma and brain tissues were harvested 30 min later for scintillation counting. The data are expressed as the ratio between tissue and plasma scintillation counts (dots per minute). Box-and-whiskers plots with the box extending from the 25th to 75th percentiles and medians (lines) are depicted. The whiskers indicate the minimum and maximum values. Statistical analysis employed Student’s t test (**, P < 0.01). (B) Cerebral blood flow assay. [14C]iodoantipyrine was administered to mice 14 h after S. epidermidis (n = 14) or saline (n = 15) injection. Plasma and brain tissues were harvested 30 min later for scintillation counting. The data were pooled from two independent experiments. Statistical analysis employed Student's t test. (C and D) Mice were injected with saline or S. epidermidis. At various times postinfection, mice were sacrificed and perfused with saline, and brains were harvested for cytokine detection with a multiplex cytometric bead array (saline, n = 6; S. epidermidis, n = 8) (C) and caspase 3 activity analysis by cleavage of fluorometric substrates (saline, n = 7 to 14; S. epidermidis, n = 10 to 12) (D). Means plus SD are plotted. Statistical analysis employed two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni post hoc test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).