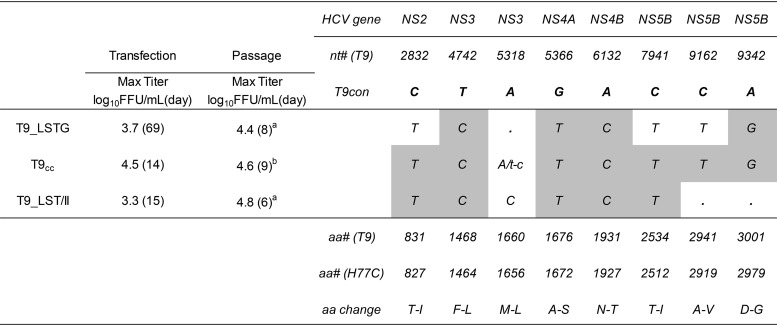
TABLE 1.
Characteristics of T9(2a) HCV cell culture-adapted recombinant viruses in transfection and passage in Huh7.5 cellsa
Max Titer, the highest infectivity titer observed (at the time points given in parentheses); a, passage 3; b, passage 2. Letters indicate dominant coding nucleotide changes. A single capital letter indicates that the nucleotide was the only one observed in the sequence. Coding changes as quasispecies (accounting for 50% of the base call) were found only in T9_LSTG and included T2973T/C (amino acids I-I/T), T6812T/C (amino acids F-F/L), T7394T/G (amino acids F-F/V), and C8370C/T (amino acids T-T/I). Two noncoding dominant changes were observed in T9_LSTG: A3730G and T9229C. No noncoding changes were observed in T9cc or T9_LSTG/II. The gray shading indicates the mutations that were engineered in the specific recombinant, which were maintained in the viruses in all cases. T9con indicates the nucleotides found in the consensus ORF sequence (nonadapted) of strain T9. nt# (T9) and aa# (T9) indicate the nucleotide and amino acid numbers, respectively, according to the molecular clone of T9 (see Materials and Methods). aa# (H77C) indicates the amino acid number according to the polyprotein of reference strain H77C (GenBank accession number AF011751). aa change indicates the amino acid changes in the polyprotein of the T9 consensus sequence induced by the nucleotide changes depicted in the body of the table.