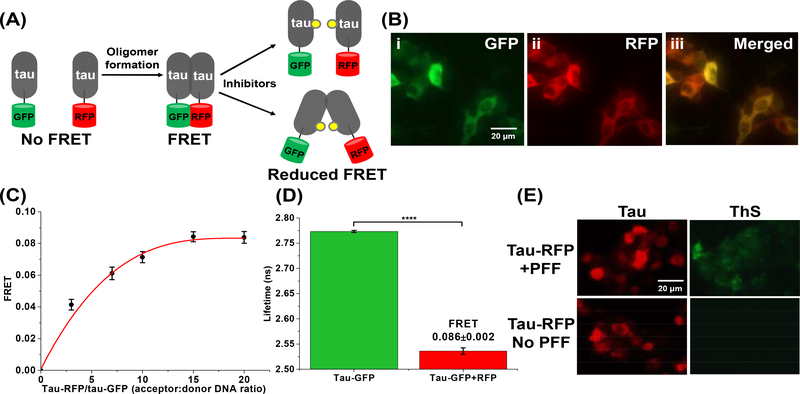
Fig. 2: The tau inter-molecular FRET biosensor and fluorescence lifetime technology enable direct monitoring of tau oligomerization in cells.
(A) Schematic representation of live-cell based tau inter-molecular FRET biosensor. FRET signal is observed when tau oligomers form, which can be modulated by small-molecule inhibitors. Tau oligomer is drawn as a dimer for illustration but it can be any species more than a dimer (≥2-mers). (B) Fluorescence microscopy images of (i) GFP channel, (ii) RFP channel and (iii) merged channel of HEK293 cells expressing tau-GFP/RFP (tau FRET biosensor). (C) Titration of tau-RFP (acceptor) to tau-GFP (donor) illustrates that the FRET efficiency of the biosensor follows a hyperbolic dependence on acceptor concentration. (D) Fluorescence lifetime measurements of the tau biosensor show efficient FRET, indicating tau self-association. (E) Thioflavin-S (ThS) staining of HEK293 cells expressing tau-RFP (in same total DNA concentration as used in the FRET biosensor) in the presence and absence of the positive control of tau preformed fibrils (PFF). Data are means ± SD of three independent experiments. ****P < 0.0001 by two-tailed unpaired t test.