Fig. 2.
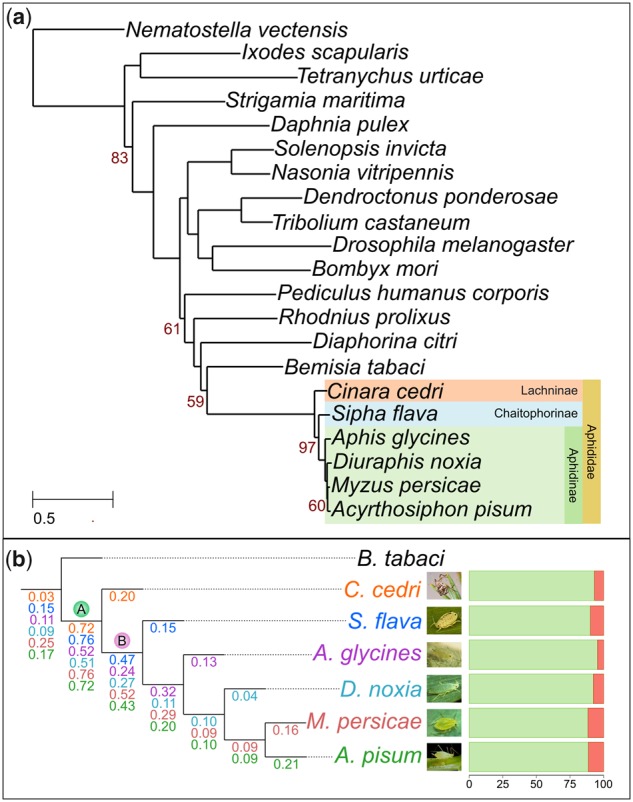
Species tree and duplication ratios of the six phylomes. (a) Phylogenetic tree obtained from the concatenation of 57 widespread gene families. In yellow, all the individuals included in this study that belong to the family Aphididae; in green, light blue, and orange, the aphids that belong to the subfamily Aphidinae, Chaitophorinae, and Lachninae, respectively. All omitted bootstrap values are maximal (bootstrap 100%). (b) Zoom out showing the duplication ratios per each phylome: Cinara cedri—orange, Sipha flava—blue, Aphis glycines—purple, Diuraphis noxia—light blue, Myzus persicae—red, Acyrthosiphon pisum—green. The two branches with the higher duplication ratio are marked as A (ancestral to all six aphids) and B (after the divergence of C. cedri and ancestral to the other five aphids). Bars on the right show the percentage of proteins (orange) associated with transposons in each aphid species. Bemisia tabaci is the outgroup.
