Figure 1. Overview of sorting and isolating aptamer-labeled target cells followed by antidote treatment to remove the aptamer and generate ligand-free cells.
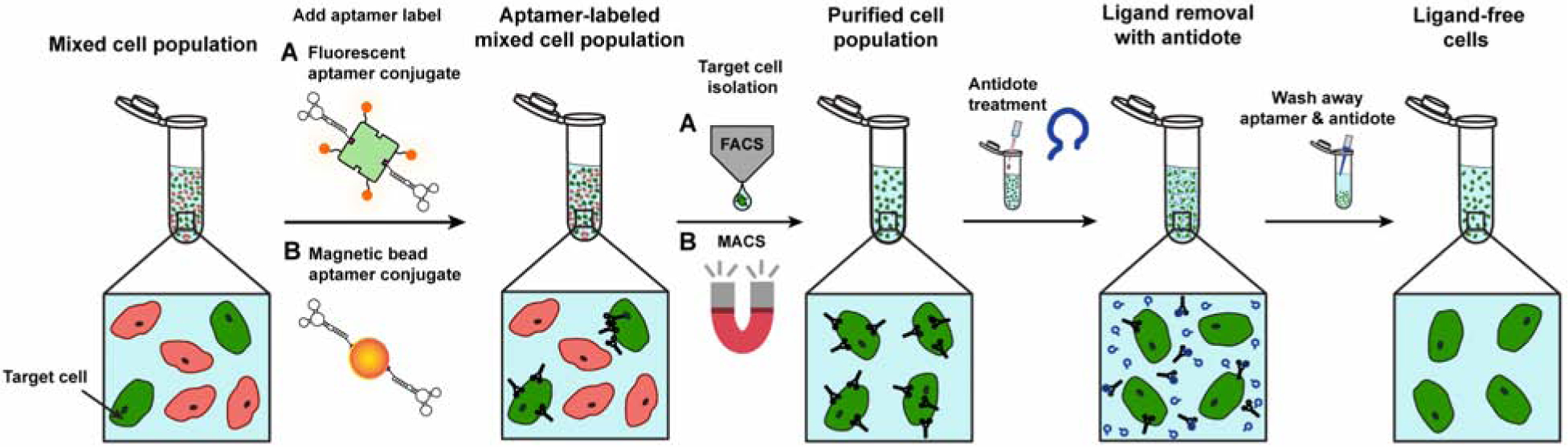
Target cells of an initially heterogenous population are selectively labeled with a fluorescent dye tagged-aptamer (A) or with aptamer-magnetic beads (B) and then isolated using a conventionally antibody-based purification scheme such as FACS or MACS, respectively. However, the utility of purified target cells may be compromised as residual sorting ligand on purified cells can interfere with their native functions or elicit an immune response. Unlike antibody-based labels, treatment of aptamer-labeled cells with matched antidotes allows for ligand removal, returning cells to a ligand-free, native functional state.
