Figure 5. The E07 Aptamer-Antidote Pair Can Be Used to Reversibly Stain and Restain EGFR(+) Cells, Creating a Molecular Sorting Switch.
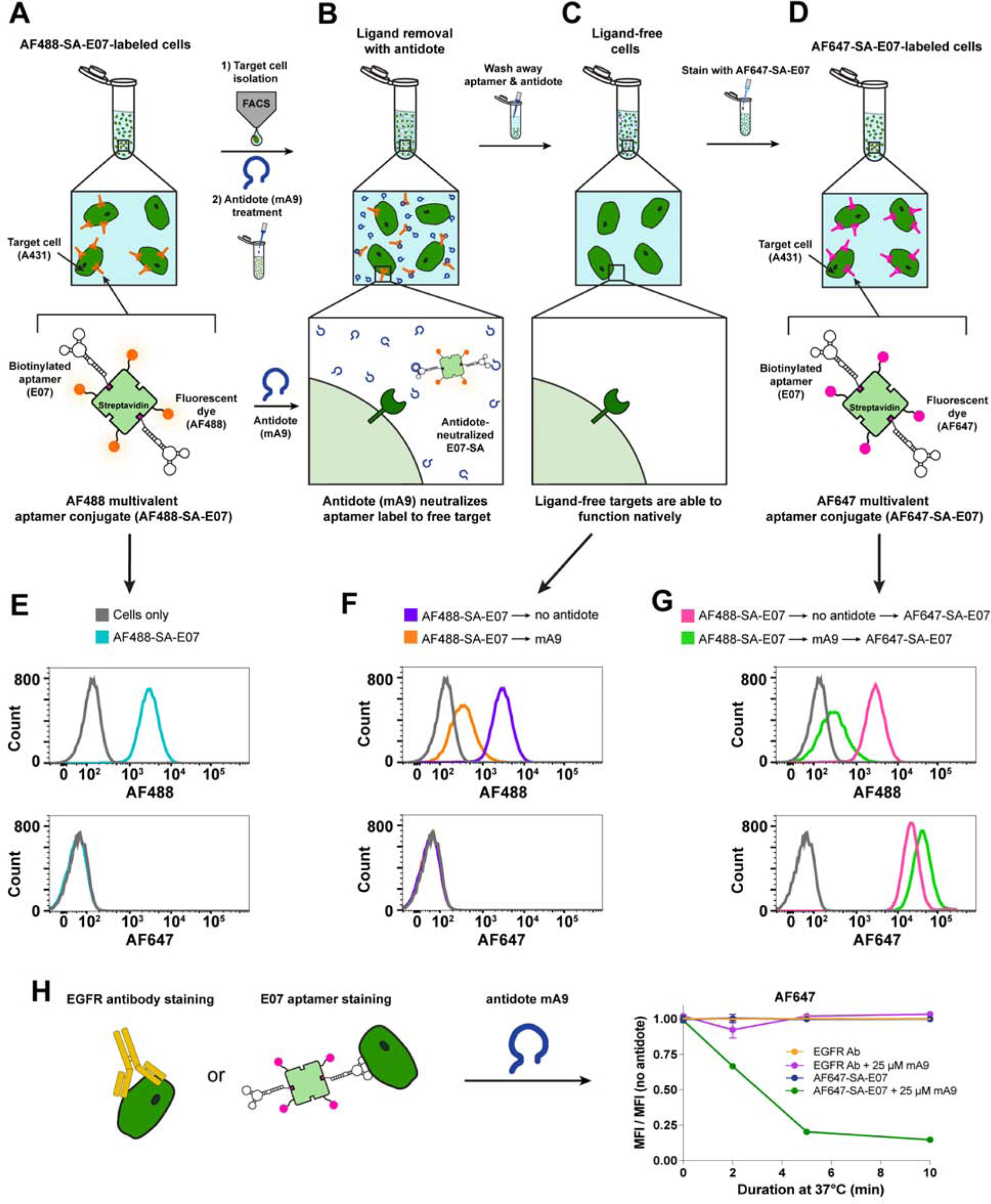
(A–D) Overview of AF488-SA-E07 aptamer-staining and FACS sorting of EGFR(+) cells followed by antidote treatment to remove the E07 stain and leave the cells free for additional staining with a different E07 label. (A) EGFR(+) A431 cells were stained with the green-fluorescent AF488-SA-E07, sorted for E07/AF488+ signal and then (B) destained with antidote mA9 to (C) generate a pool of ligand-free unlabeled cells that could be (D) subsequently restained with E07 labeled with the far-red-fluorophore AF647-SA. (E–G) Small aliquots were saved at each of these steps for subsequent analysis by flow cytometry. (E) AF488-SA-E07 bound and stained EGFR(+) A431 cells, allowing for FACS sorting based on AF488 signal. (F) mA9 antidote treatment of sorted AF488(+)/EGFR(+) cells removed ~ 90% of the AF488-SA-E07 stain. (G) The resultant label-free cells were restained with AF647-SA-E07, generating ~80% more AF647 signal compared to the cells that were not antidote destained. (H) mA9 enhanced removal of AF488-SA-E07 over time but did not affect the EGFR-binding antibody ICR10 as evidenced by flow cytometry analysis of stained A431 cells. A431 cells were labeled with a 1:2000 dilution of antibody ICR10 or with 100nM AF488-SA-E07 at 4°C, and then incubated with 250-fold excess of mA9 antidote for different lengths of time at 37°C. Shown is the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the antibody or aptamer signal after antidote treatment normalized to the MFI of the respective treatment without antidote treatment. (n=3 for all studies; representative curves shown, all flow data shows ≥ 104 gated events) See also Figure S1B and Figure S5.
