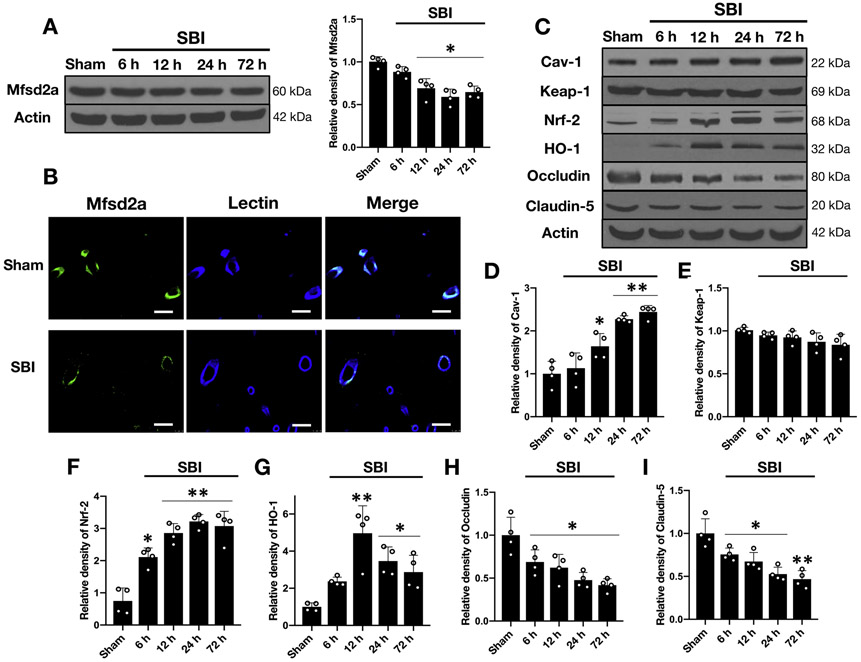
Figure 3:
Temporal expression of endogenous Mfsd2a, cav-1, Keap-1, Nrf-2, HO-1, occludin and claudin in the rFPA following SBI
A) Representative Western blot images and quantitative analyses of endogenous Mfsd2a in the rFPA revealed significantly decreased expression of Mfsd2a following SBI. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. n= 4/group. ANOVA, Tukey. *p<0.05 compared to Sham.
B) Representative immunostaining images for Mfsd2a (green) and lectin (blue) positive endothelial cells in the brain microvessels from Sham and SBI animals (rFPA) at 24 hours following the injury. The merged images of the overlay of Mfsd2a together with lectin are seen as cyan. Scale bar= 50 μm. n= 1/group.
C) Representative Western blot images and quantitative analyses of endogenous pathway proteins in the rFPA following SBI revealed increased expression of cav-1 (D), Nrf-2 (F) and HO-1 (G) while Keap-1 levels did not change significantly over 72 hours (E). The protein levels of occludin (H) and claudin-5 (I) were significantly reduced starting at 6 hours after SBI and remained low up to 72 hours. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. n= 4/group. ANOVA, Tukey. **p<0.001 compared to Sham, *p<0.05 compared to Sham.
SBI: Surgical brain injury