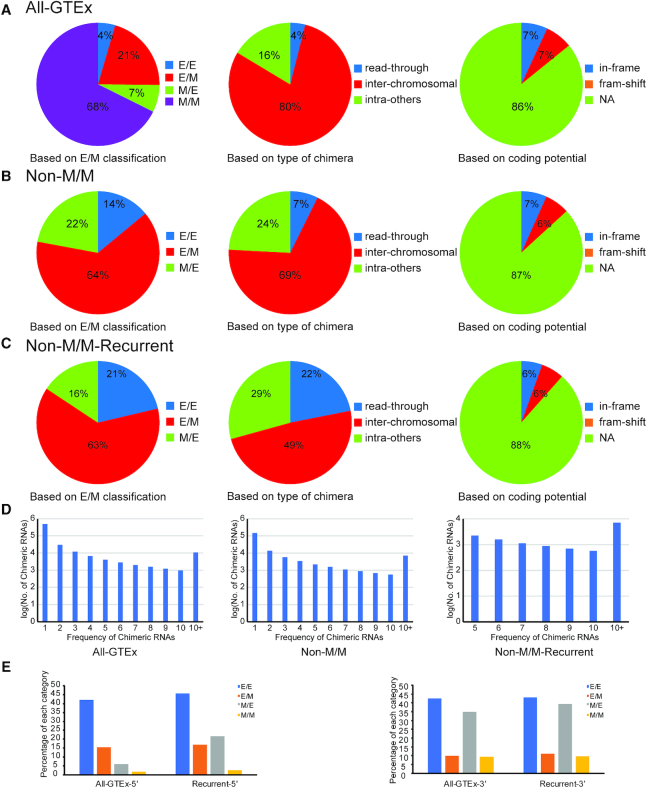
Figure 3.
Distribution of chimeric RNAs in different EM categories, types of chimeras based on parental gene location, and fusion protein coding potential. The distribution of chimeric RNAs was examined at three stages along our filtering pipeline: All GTEx predictions (All-GTEx) (A), after removal of M/M (Non-M/M) (B), and with an additional frequency requirement (Non-M/M-Recurrent) (C). The number of chimeric RNAs is also plotted based on their frequency (D). (E) Percentage of chimeric RNAs harboring the canonical splicing donor sequence (AG/GT) at the 5′ junction (left) or canonical splicing acceptor sequence (AG/G) at the 3′ junction (right) is plotted. All four categories of chimeric RNAs (E/E, E/M, M/E and M/M) in the whole GTEx or recurrent groups were examined.