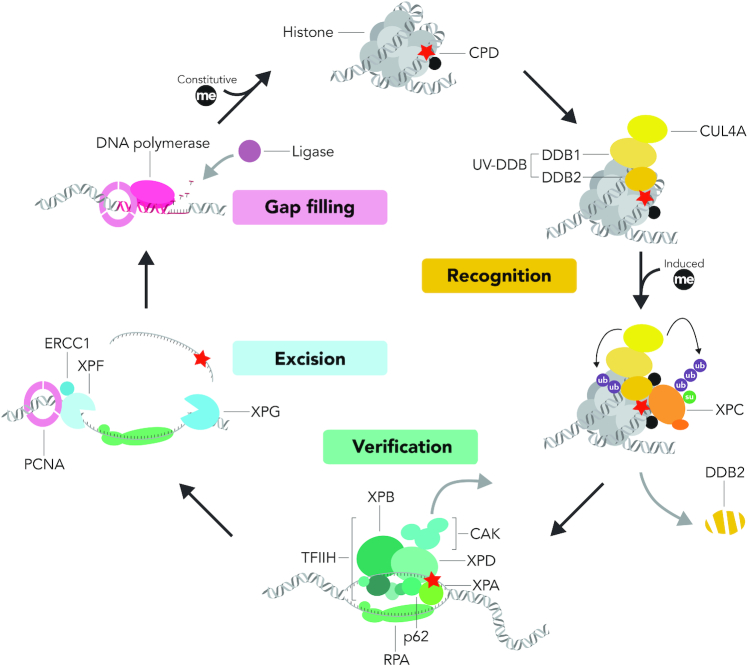
Figure 1.
GG-NER reaction in chromatin. This scheme summarizes the major transitions of the GGR reaction cycle (from DNA damage recognition to the final DNA gap filling) and the ‘access-repair-restore’ model describing how this multistep process may take place in the nucleosome landscape of chromatin. The XPC subunit initiates GGR activity as part of a trimeric complex with HR23B and CETN2. KMTs favor the GGR reaction in the nucleosome context by constitutive and DNA damage-induced depositions of histone methylation marks.