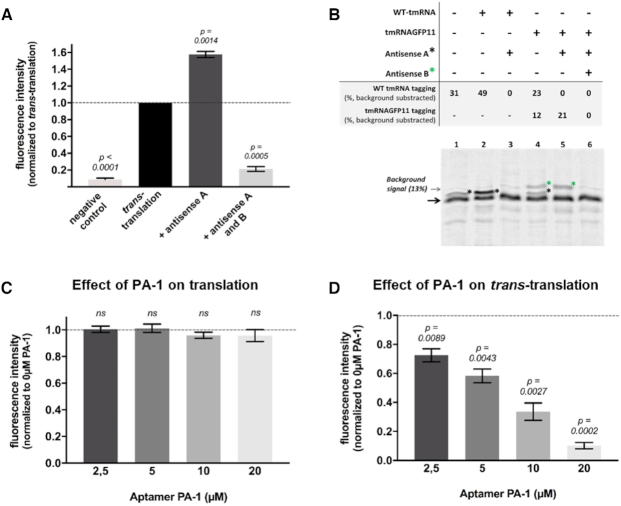
Figure 2.
Quantification of in vitro trans-translation in the presence of inhibitors by fluorescence and radioactivity assays. (A) Fluorescent assay. The ‘negative control’ contains all trans-translation components except tmRNAGFP11; ‘trans-translation’: same as negative control with tmRNAGFP11; ‘Antisense A’ and ‘Antisense A and B’: same as ‘trans-translation’ respectively with an antisense targeting WT tmRNA or an antisense targeting tmRNAGFP11 (Supplementary Table S1). (B) Radioactive assay. Trans-translation reactions were performed as in fluorescent assays but using a non-stop DHFR instead of truncated GFP and [35S]-methionine (see methods). The non-stop DHFR is indicated by a black arrow and the lower-mobility trans-translated DHFR proteins bands are indicated by a black or a green star, depending on their tagging by WT tmRNA or tmRNAGFP11, respectively. (C) In vitro translation assays. Effect of SmpB peptide aptamer PA-1 on in vitro translation tested at final 2.5–20 μM concentrations. For experiments, the PURExpress® kit basal fluorescence was subtracted from the measurements and the results are then normalized with respect to the translation control (symbolized with the black dotted line). A t-test was performed using that control hypothetical value. Bars represent standard deviation of at least three independent experiments. ‘ns’ is for non-significant (D) In vitro trans-translation assays. Peptide aptamer was added at the same concentration than in translation assays. For these experiments, measurements were normalized with respect to the trans-translation control (‘Antisense A’) without any compounds (symbolized with the black dotted line). A t-test was performed using that control hypothetical value. P-values indicates significant differences compared to the control. Bars represent standard deviation of at least three independent experiments.