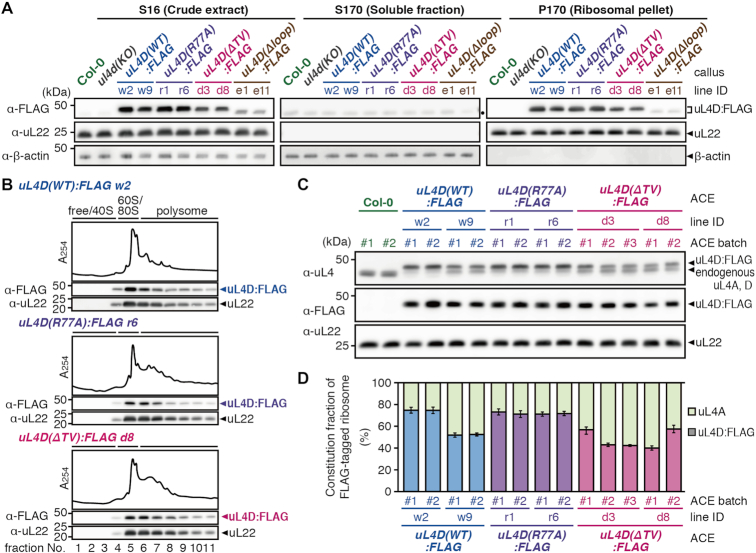
Figure 4.
Functionality and constitution fraction of FLAG-tagged mutant uL4D-containing ribosomes. (A) Crude extracts (S16), post-ribosomal supernatants (S170), and ribosomal pellets (P170) prepared from callus cultures derived from wild-type Col-0 plants, ul4d(KO), and FLAG-tagged mutant uL4D transgenic lines are shown. Total proteins (10 μg in S16/S170; 1 μg in P170) were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG antibody, anti-uL22 antiserum, and anti-β-actin antiserum. Positions of FLAG-tagged uL4D mutant proteins (uL4D:FLAG), 19-kDa uL22, and 43-kDa β-actin bands are marked. β-Actin was used as a soluble protein marker. Note that uL4D(Δloop):FLAG protein is smaller than uL4D(WT):FLAG by ∼1 kDa due to a 13-amino acid-deletion. A black dot in S170 marks the cross-reaction band. Representative results of two biological replicates are shown. (B) P-170 fractions from uL4D(WT):FLAG w2 line, uL4D(R77A):FLAG r6 line, and uL4D(ΔTV):FLAG d8 line were fractionated by ultracentrifugation through a 15–60% (w/v) sucrose density gradient. UV absorbance profile at 254 nm and immunoblot analysis using anti-FLAG antibody and anti-uL22 antiserum are shown. Positions of free proteins and 40S subunit, 60S subunit, 80S ribosome and polysome fractions are indicated. Representative results of two biological replicates are shown. (C) Immunoblot analysis of ACE batches using anti-uL4 antiserum, anti-FLAG antibody, and anti-uL22 antiserum. Representative results of three technical repeats are shown. Anti-uL4 detects both FLAG-tagged mutant uL4D and endogenous uL4A. (D) Immunoblot signals obtained using anti-uL4 antiserum in (C) were quantified, and the constitution fractions of FLAG-tagged uL4D-containing ribosomes among total ribosomes were calculated. Means ± SD of three technical repeats are shown.