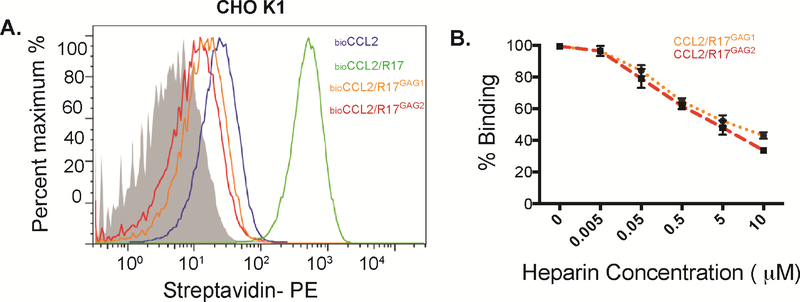
Figure 5. R17 inhibits CCL2 interaction with cell surface GAGs.
(A) FACS analysis monitoring the effect of wild type R17, R17GAG1 and R17GAG2 on the interaction of CCL2 with cell surface GAGs as measured by changes in MFI (mean florescence intensity). 50nM of biotinylated CCL2 was added to CHOK1 cells in the presence or absence of 100nM R17GAG1 (orange line) 100nM R17GAG2 (red line) or 100nM wild type R17 (blue line). Cell surface bound CCL2 was detected with Streptoavidin-PE using FACSCalibur (BD Biosciences) and data analyzed with FlowJo. Representative histogram plot shows inhibition of CCL2-GAG interactions by R17GAG1 and R17GAG2. (B) R17 competes with soluble heparin sulfate for chemokine binding. R17GAG1 and R17GAG2 was immobilized to a CM5 chip and mCCL2 was injected at a concentration of 100 nM alone or in combination with the indicated increasing concentrations of heparin sulfate (0, 50nM, 500nM, 1μM, 5μM and 10μM). The error bars represent the standard error of three independent experiments.