Figure 1.
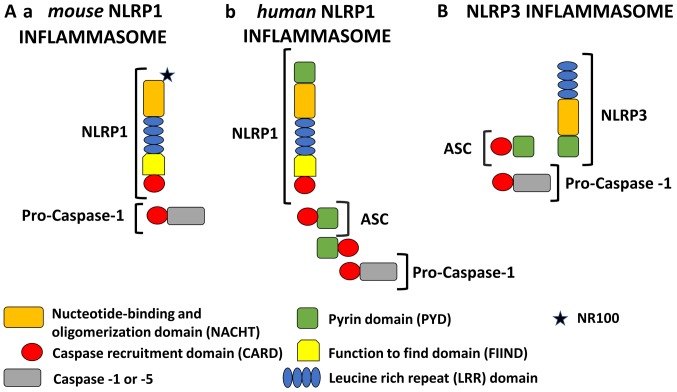
Schematic representation of NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes. All NLRP1 inflammasomes are composed of NACHT, LRR, FIIND and CARD domains. Domain positions are indicated to scale. The presence of FIIND and CARD domains at the C-terminus makes NLRP1 stand out from all other members of the NLR family. However, the NLRP1 inflammasome is quite different in murine and human models. (A-a) Mouse NLRP1 inflammasome: In mice, there are three paralogs of NLRP1 (Nlrp1a, -b, and -c) which contain an NR100 domain instead of the PYD found in humans. Mouse NLRP1 can activate caspase-1 directly and ASC (apoptosis associated with Speck-like protein) is not required. (A-b) Human NLRP1 inflammasome: Human NLRP1 contains the N-terminal PYD. Its activity is dependent upon ASC, which is associated with the C-terminal CARD domain. (B) NLRP3 inflammasome: The NLRP3 inflammasome consists of an NLRP3 protein, an ASC adaptor, and procaspase-1. Upon stimulation, NLRP3 and ASC adhere via their PYD domains, whereas ASC and caspase-1 adhere via their CARD domains. Therefore, NLRP3 forms an ASC-dependent inflammasome. NLRP1, NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 1; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3; NACHT, nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain; LRR, leucine rich repeat; FIIND, function to find domain; PYD, pyrin domain; ASC, apoptosis associated with Speck-like protein.