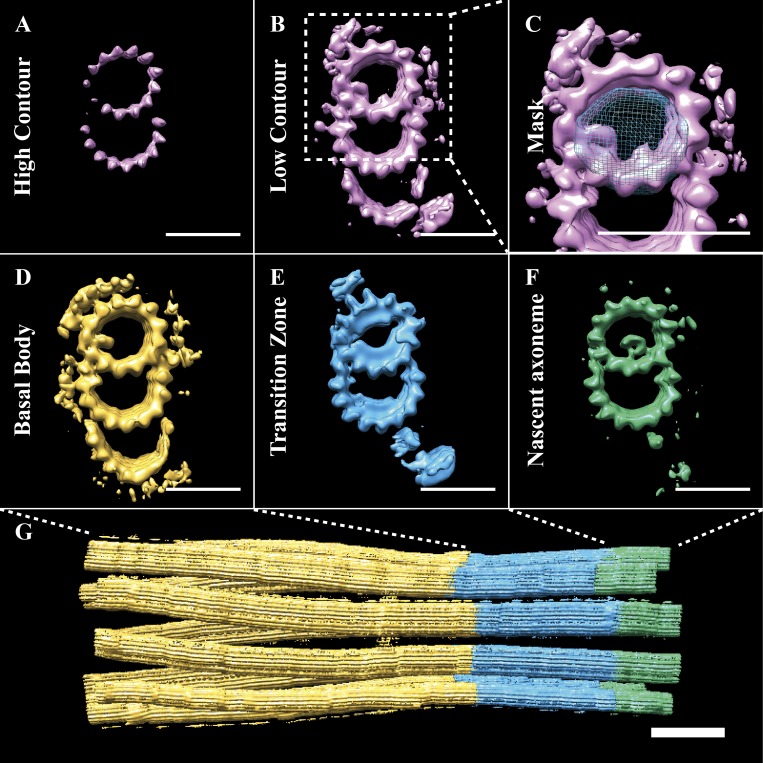
Figure 4.
A-tubule MIPs divide the cilium base into three subdomains. (A and B) At high contour (A), the whole-population map showed density for the A- and B-tubules, while at lower contour (B), the map also showed density for the C-tubule and many microtubule binding proteins. Classification of the subvolume population based on A-tubule MIPs (C; mask in blue) gave three major classes (D, E, and F) accounting for >90% of the data. (D) The largest class (∼61%) was composed of a TMT, with a characteristic bilobed MIP within the A-tubule. We defined this class as the BB. (E) The second most populous class (∼21%) showed a DMT, with extensive MIPs within the A-tubule, which we defined as the TZ. (F) The smallest class (∼10% of data) was a DMT, with a tube-like density inside the A-tubule. Its position relative to the appearance of the central pair MTs in the raw tomograms suggested that this was the nascent axoneme. (G) The extent of the BB, TZ, and axoneme subdomains. Scale bars are 25 nm (A–F); 100 nm (G).