Figure 3.
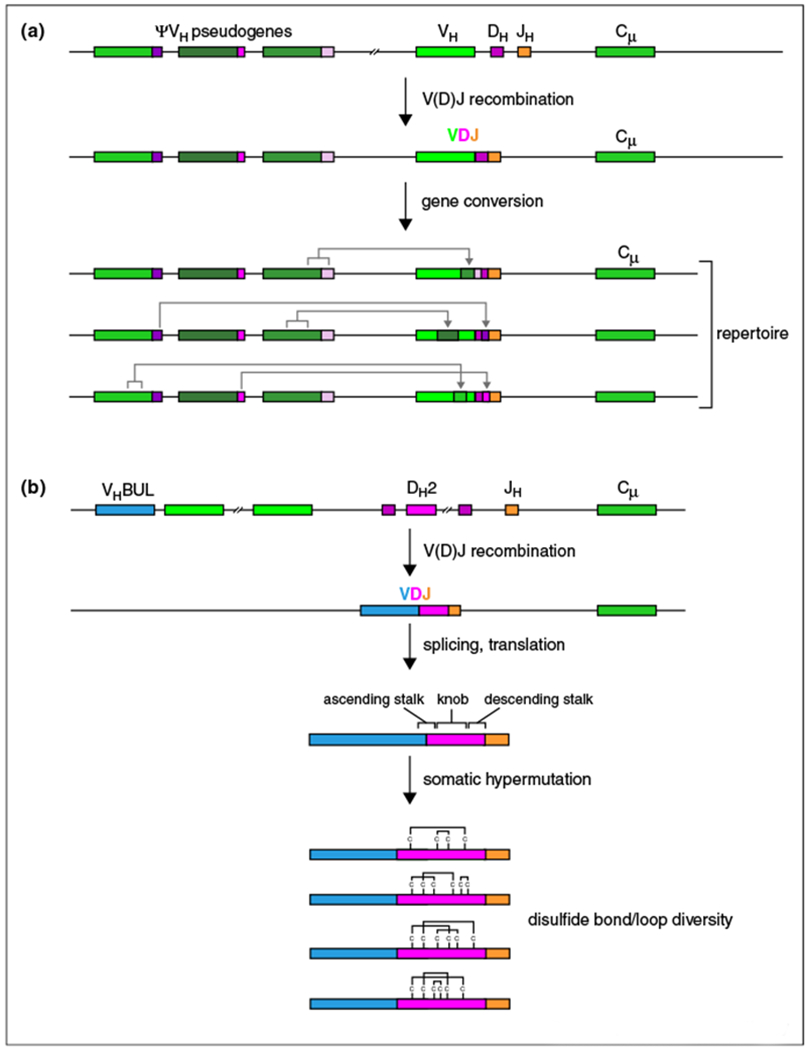
Novel processes for producing genetic diversity in chickens and cows. (a) Unlike humans or mice, chickens use a gene conversion strategy to create a diverse antibody repertoire. A single VDJ event occurs on the heavy chain locus, followed by gene conversion using sequence homology from a number of 5′ pseudogenes (ψVH) which can be in rearranged form and donate diverse genetic fragments into the rearranged V region. (b) Ultralong CDR H3 and repertoire development in the cow. Cow antibodies with ultralong CDR H3s appear to use only one VH region, VHBUL, which recombines with a long D region, DH2 to produce a germline VDJ recombined V-region. The single rearrangement then undergoes somatic hypermutation which may mutate residues to or from cysteine, changing the disulfide patterns of the repertoire, in addition to adding sequence diversity.
