Figure 1.
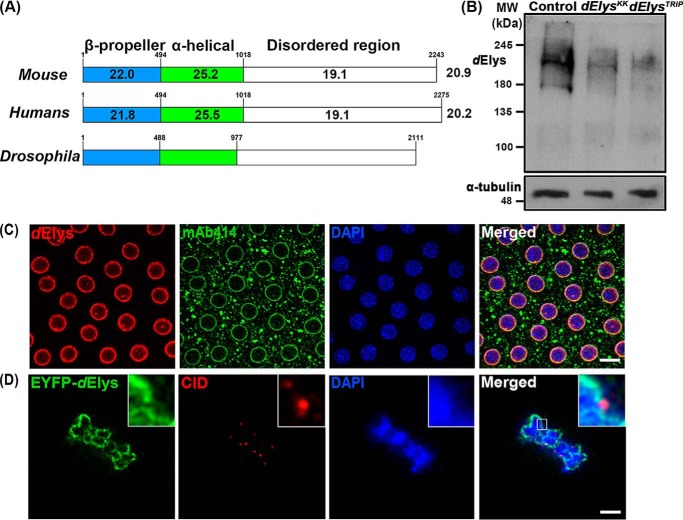
ELYS is conserved in Drosophila. A, graphical representation of sequence identity of dElys with mouse and human ELYS. dElys is 20.9 and 20.2% identical with mouse and human ELYS, respectively. Domain-wise identity is mentioned in each domain. Conserved secondary structures between Drosophila, mouse, and human ELYS are represented. β-Propeller N-terminal domain, α-helical central domain, and disordered C-terminal regions are conserved in dElys as in higher orthologs. B, antibody generated against dElys identified a band of ∼215 kDa in lysates obtained from third instar larval head complex from WT control and ubiquitous dElys knockdown lines as indicated. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. C, syncytial Drosophila embryos stained with dElys antibody (red), mAb414 (green) marking FG-nucleoporins, and DNA stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 5 μm. D, high-resolution image of metaphase-arrested Drosophila S2-expressing EYFP–tagged dElys (green) stained for kinetochores with an anti-CID antibody (red). Scale bar, 2 μm.