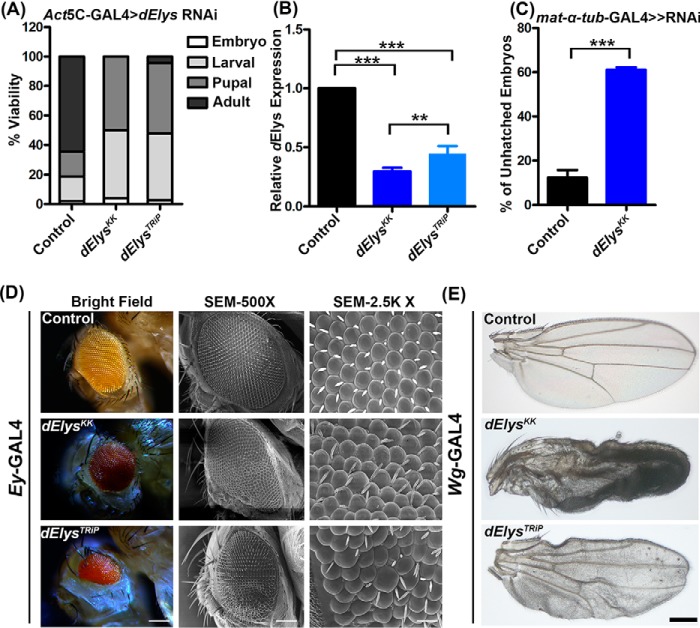
Figure 2.
dElys is essential for the normal development of Drosophila. A, quantification representing the lethality stages of the dElys knockdown organism. RNAi lines were driven with ubiquitous Act5C–GAL4 driver. Control represents WT flies crossed with the Act5C–GAL4 driver. B, quantitative PCR for dElys knockdown using two different RNAi lines. Data are represented from at least three independent experiments. Statistical significance was derived from one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. Error bars represent S.E. *** represents p < 0.0001, and ** represents p < 0.001. C, hatching rate analysis of maternal depletion of control and dElys in embryos using mat-α-tub-GAL4 ≫ RNAi driver. D, eye-specific knockdown of dElys using the Ey-GAL4 drivers. The 1st column shows the stereomicroscopic image; the 2nd column represents the SEM image (×500), and the 3rd column shows an SEM image (×2.5K). Observations were made from at least three independent experiments. Scale bar, 200 μm in the stereomicroscopic image; 20 μm in SEM column 1, and 2 μm in SEM column 3). Control represents WT flies crossed with Ey-GAL4 driver. E, dElys depletion in the wing using the Wg-GAL4 driver. Representative images are shown for wing phenotypes. Observations were made from at least three independent experiments. Scale bar, 200 μm. Control is WT flies crossed with Wg-GAL4driver.