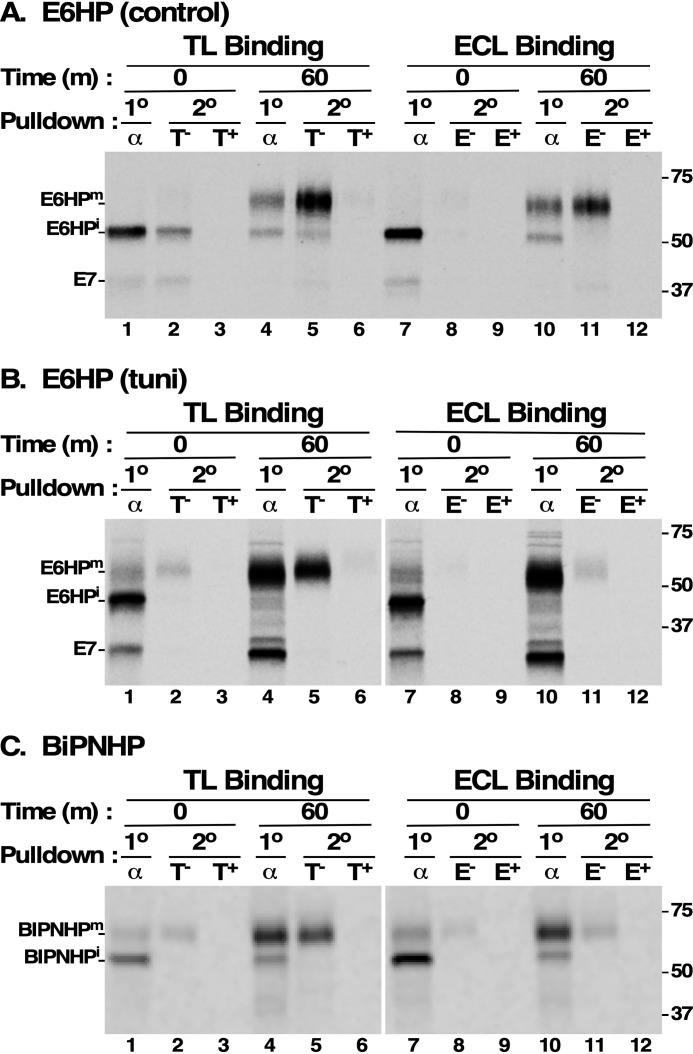
Figure 8.
Sequential pulldown of E6HP and BiPNHP with lectins. Cultured BSF trypanosomes (107 cell equivalents/lane) expressing E6HP (A and B) or BiPNHP (C) were [35S]Met/Cys pulse-chase (15/60 min) radiolabeled in the presence of FMK024 (20 μm). As indicated, tunicamycin was included to block N-glycosylation (B, tuni). Cell extracts were prepared as described in Fig. 3. E6HP and BiPNHP polypeptides were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies (α), and then solubilized lysates were affinity-selected (2°) with TL:Bio (T, left) or ECL:Bio (E, right) in the absence (−) or presence (+) of competing chitin hydrolysate (1:1000) or lactose (200 mm), respectively. The mobilities of mature (m) and immature (i) E6HP and BiPNHP species are indicated on the left, and molecular mass standards are indicated on the right (kDa). Measured conversion of normal E6HPi to E6HPm is ∼12 kDa (A, lane 1 versus lane 4); measured conversion of non-N-glycosylated E6HP is ∼7 kDa (B, lane 1 versus lane 4); and measured conversion of BiPNHPi to BiPNHPm is ∼10 kDa (C, lane 1 versus lane 4).