Figure 3.
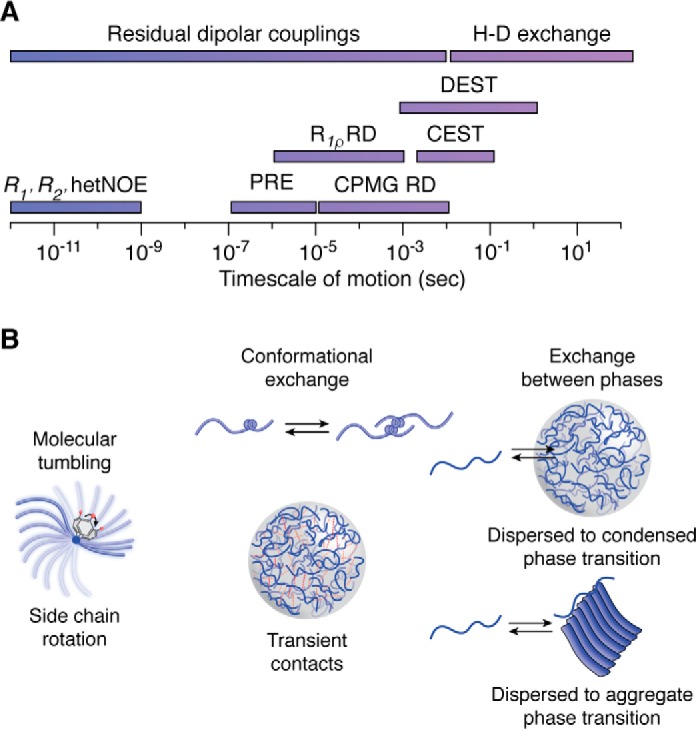
NMR timescale of motion for studying the dynamics of LLPS systems. A, various types of NMR experiments can probe for processes from the picosecond to second timescale. B, fast motions (picosecond-to-nanosecond) that involve overall molecular tumbling and fluctuations of the peptide backbone and side-chain rotations can be measured using R1, R2, and heteronuclear NOE experiments. Intermediate motion processes (microsecond-to-millisecond) that involve conformational exchange and transient contacts can be measured by a variety of experiments, such as paramagnetic relaxation enhancement, CPMG relaxation dispersion, and R1ρ. Slower processes (millisecond-to-second), such as the exchange between liquid and solid phases can be probed using saturation transfer techniques as well as hydrogen-deuterium exchange.
