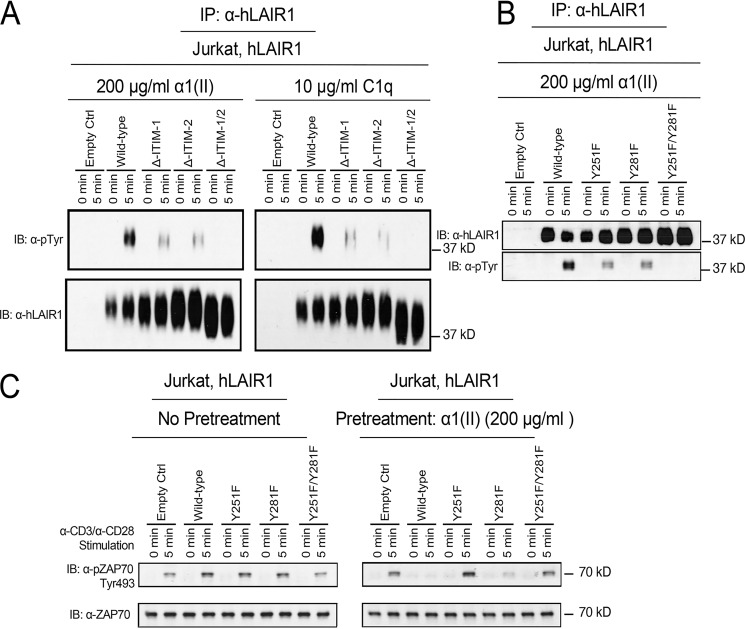
Figure 4.
Induction of tyrosine phosphorylation in ITIMs of LAIR-1 by α1(II) and its impact on TCR signaling. A, Jurkat cells expressing either an empty control, WT human LAIR-1, or ITIM-deletion mutants of LAIR-1 were activated by α1(II) or C1q for the indicated time period. LAIR-1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) from each whole-cell lysate with protein A/G beads conjugated with anti–LAIR-1 antibody. Phosphorylation of LAIR-1 in the immunoprecipitants was examined by Western blotting analysis using anti–LAIR-1 and anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies, respectively. The big ranges of hLAIR-1 on the Western blotting with anti–hLAIR-1 antibody may be explained by other posttranslational modifications, such as ubiquitination or SUMOylation. B, Jurkat cells expressing either an empty control, WT human LAIR-1, or Tyr-to-Phe point mutation at aa 251, aa 281, or both of LAIR-1 were activated by α1(II) or C1q for 5 min. LAIR-1 was immunoprecipitated from each whole-cell lysate with protein A/G beads conjugated with anti–LAIR-1 antibody. The phosphorylation of LAIR-1 in the immunoprecipitants was examined by Western blotting analysis using anti–LAIR-1 and anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies, respectively. C, Jurkat cells expressing either an empty control, WT human LAIR-1, or a Tyr-to-Phe point mutation at aa 251, aa 281, or both of LAIR-1 were pretreated media (left panel) or α1(II) (right panel) and then activated with α-CD3 and α-CD28 for 5 min. Whole-cell lysates were collected, and the phosphorylation of ZAP-70 was detected by Western blotting assay using anti-pZAP70 Tyr-493 as an indication of ZAP-70 activation. The membrane was stripped and reblotted with anti-ZAP 70 antibody. The data shown are representative of three separate analyses. IB, immunoblot.