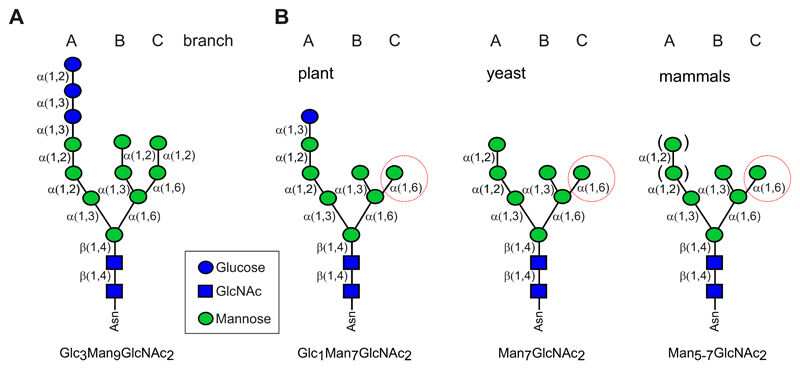
Figure 3. N-glycan structures.
(A) The transferred N-glycan is composed of three glucose, nine mannose, and two GlcNAc residues. The three branches (A, B, and C) and the linkage between the individual sugar residues are indicated. (B) Schematic representation of the proposed prevailing N-glycan structure that is present on plant, yeast or mammalian glycoprotein ERAD substrates. The exposed free α1,6-mannose residue (red circle) serves as the common glycan determinant for degradation of misfolded glycoproteins.