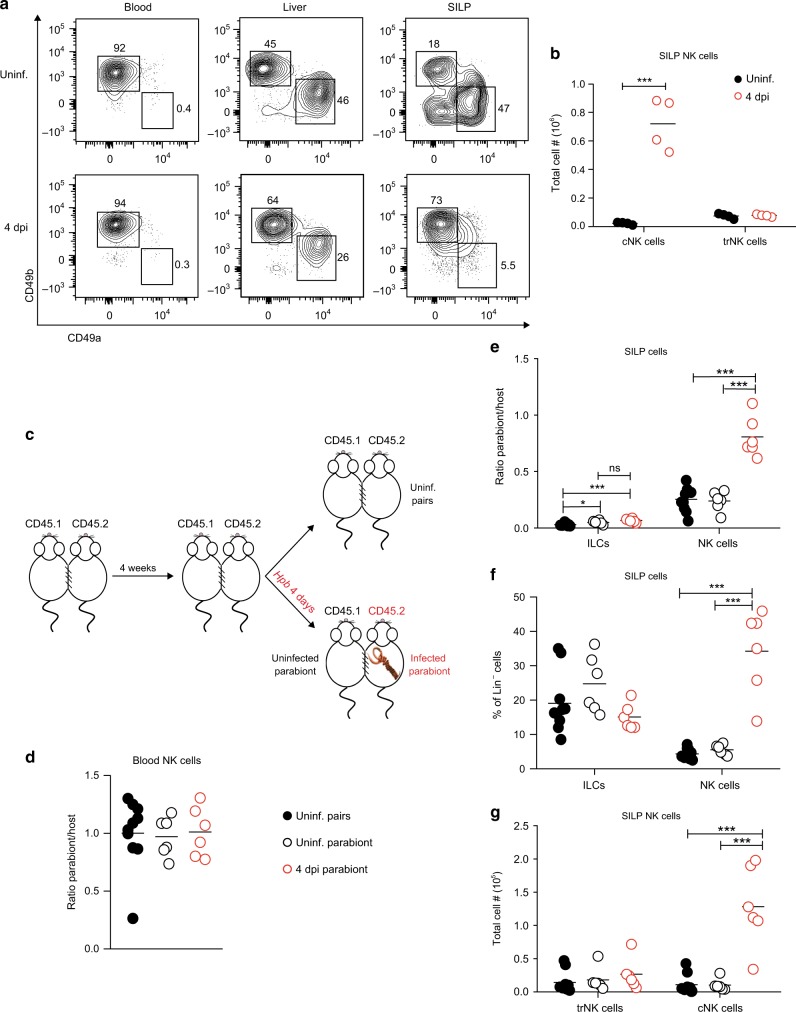
Fig. 3.
Hpb infection recruits circulating NK cells to the small intestine. a Representative contour plots of cNK cells (CD127−NK1.1+CD49a−CD49b+) and trNK cells (CD127−NK1.1+CD49a+CD49b−) in the blood, liver, and SILP of uninfected mice and 4 dpi with Hpb. b Total cell numbers of cNK and trNK cells in the SILP of uninfected mice and 4 dpi with Hpb. c Experimental design outlining the parabiosis experiments. d Ratio of Parabiont (CD45.1)/Host (CD45.2) Lin− NK cells in the blood of uninfected and 4 dpi Hpb parabiotic mice. In uninfected pairs, data from CD45.1+ and CD45.2+ parabionts were pooled. In the infected pairs, the “host” represents the CD45.2+ mouse. e Ratio of Parabiont/Host ILCs (CD127+NK1.1−) and NK cells (CD127−NK1.1+) and f frequencies of ILCs and NK in the SILP of uninfected and infected parabiotic mice. g Total numbers of trNK and cNK cells in the SILP of uninfected and infected parabiotic mice. d–g Data shown are pooled from two independent experiments. b) Data was analyzed using an unpaired parametric t test for each cell type comparing with its respective uninfected group. d–g Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post test for multiple comparisons (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001). Each dot represents an individual mouse. NS, not significant.