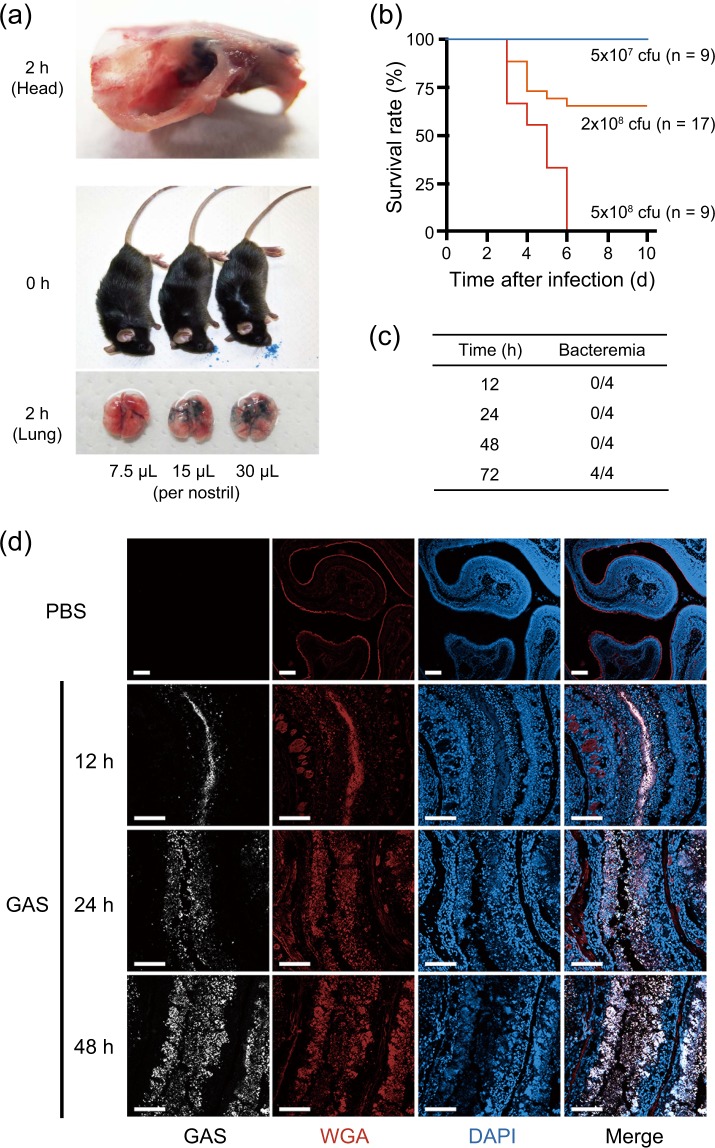
Figure 1.
Establishment of the lethal mouse model of GAS pharyngitis. (a) Inhalation range of nasal administration. (Top) Photograph of the head of a mouse 2 h after the administration of 7.5 μL of Trypan blue solution into the bilateral nasal cavities. (Middle and bottom) Photographs of the head immediately after and lung tissue 2 h after the administration of the indicated volume of Trypan blue solution into the bilateral nasal cavities. (b) Survival curves of mice intranasally infected with the ATCC 11434 strain. The survival curves of 6–7-week-old male C57BL/6 mice intranasally infected with the ATCC 11434 strain are presented (each group consisted of 9 or more mice). The survival rate of ATCC 11434 strain-infected C57BL/6 mice was dependent on the number of bacteria (Log-rank test; p < 0.01). (c) Number of mice with bacteremia after infection with the ATCC 11434 strain (n = 4 in each group). (d) The nasal cavity tissue sections of mice 12, 24, and 48 h after infection with 5 × 108 CFU of the ATCC 11434 strain were stained with an anti-GAS antibody (white), WGA (red), and DAPI (blue). PBS was inoculated as a negative control. Bars indicate 100 μm.