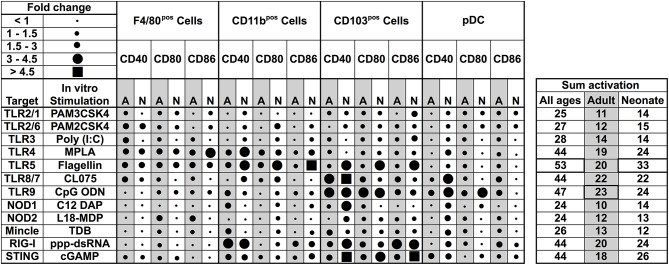
Figure 4.
Functional differences in the major APC subsets in mice lungs identify flagellin and 2′3′-cGAMP as potential activators of mucosal immunity in early life. Summary of flow cytometry all APCs maturation data collected ex vivo stimulation. Dot sizes indicate the fold-change (ranging from <1 to >4.5) for CD40, CD80, and CD86, per F4/80, CD11b, CD103 PDCA-1 APC subsets, as compared with un-stimulated controls per age group. Gray-shaded sections indicate adult data. Combined activation total fold-changes are summarized in the right panel. Upon stimulation with PRR agonists TLR2/1 (PAM3CSK4), TLR2/6 (PAM2CSK4), TLR3 (Poly I:C), NOD1, and NOD2 ligands (C12-iE-DAP and L18-MDP, respectively), APC subsets were moderately activated. Contrary to these ligands, the TLR5 agonist flagellin and STING agonist 2′3′-cGAMP specifically and robustly activated neonatal CD103+ and CD11b+ DC subsets, while the TLR4, TLR8/7, TLR9, and RIG-I (5′ppp-dsRNA) demonstrated comparable activity for all the DC subsets from the neonates and adult mice. n = 5 per age group.