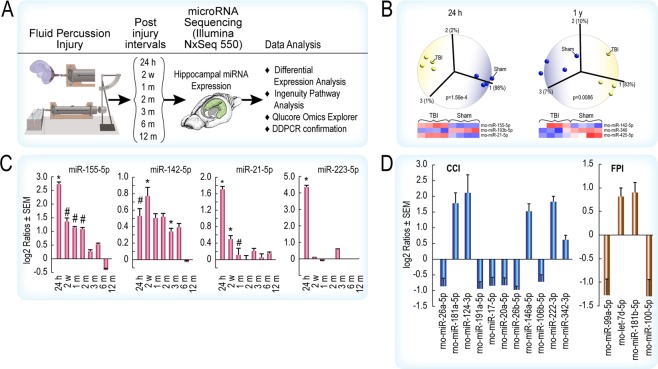
Figure 1.
(A) Experimental workflow for miRNA-seq analysis of rat hippocampus after fluid percussion injury (FPI). (B) Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed miRNAs capable of discriminating between TBI and sham-injured controls at 24 h to 1 y post FPI. (C) Analysis of miRNA-seq data in EdgeR and DESeq2 (using both the Wald test and LRT [Likelihood-ratio test] in each) identified four miRNAs that were significantly different compared to sham injured controls in at least one post-injury interval. The *denotes significant [FDR < 0.05] differential expression in both Wald and LRT tests and #denotes significant [FDR < 0.05] differential expression per Wald or LRT test. (D) Differentially expressed rat serum miRNAs that are significant compared to sham-injured rats by PCR array analysis after FPI or CCI. Data are displayed graphically as the log2 ratio ± SEM along the y-axis and miRNAs are listed along the x-axis. Data were analyzed through the use of IPA (QIAGEN Inc., https://www.qiagenbioinformatics.com/products/ingenuitypathway-analysis) and Qlucore Omics Explorer.