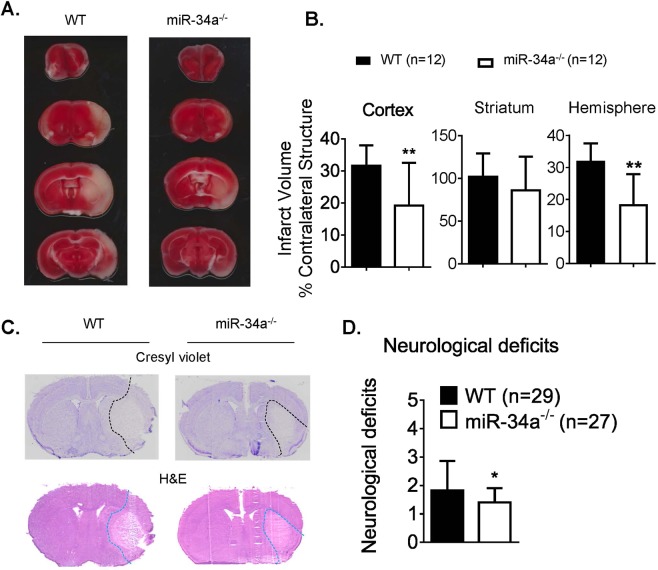
Figure 3.
miR-34a depletion reduces stroke infarction and improves neurological deficits. (A) Representative TTC staining from WT and miR-34a−/− mice following 1 h tMCAO and 24 h reperfusion. (B) Quantified infarct volumes showed a significant decrease in miR-34a−/− mice, **p < 0.01 WT vs miR-34a−/− mice (n = 12 per group). Student’s t test (two-tailed) was used for data analysis. (C) Representative Cresyl violet staining (infarction outlined by black dash lines) and H&E staining (infarction outlined by blue dash lines) from coronal brain sections of WT and miR-34a−/− mice following 1 h tMCAO and 24 h reperfusion. (D) Neurological deficits of animals generated data for stroke infarction and BBB permeability at 6 h and 24 h end-points. *p < 0.05, WT (n = 29) vs miR-34a−/− (n = 27) mice. Student’s t test (one-tailed) was used for data analysis. Data are expressed as mean ± S.D.