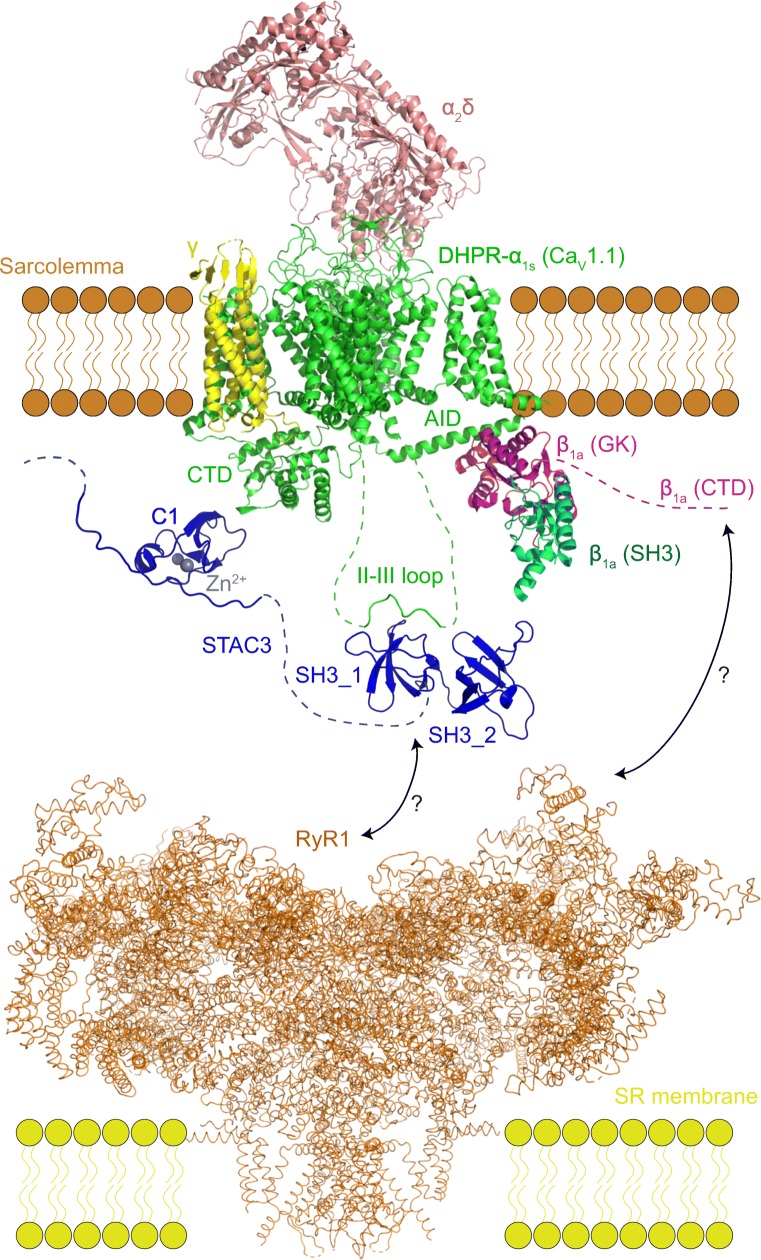
Fig. 4.
Overview of the proteins and interactions involved in the excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. The cartoon is based on the cryo-EM structure of the DHPR complex (PDB 5GJV) (Wu et al. 2016), cryo-EM structure of RyR1 (PDB 3J8E) (Zalk et al. 2015), X-ray structure of the tandem SH3 domain of STAC2 in the complex with the II–III loop peptide (PDB 6B27) (Yuen et al. 2017) and the NMR structure of the C1 domain of STAC3 (PDB 2DB6). The established interactions include those between the GK domain of DHPR-β1a and the AID peptide of the DHPR-α1s I–II loop (Norris et al. 2017), between the C1 domain of STAC3 and the C-terminal domain (CTD) of DHPR-α1s (Campiglio et al. 2018a; Campiglio and Flucher 2017), and the interaction between the central part of the II–III loop and the first SH3 domain of STAC3 (Polster et al. 2018; Yuen et al. 2017). Interactions of RyR1 with either DHPR or STAC3 remain ambiguous