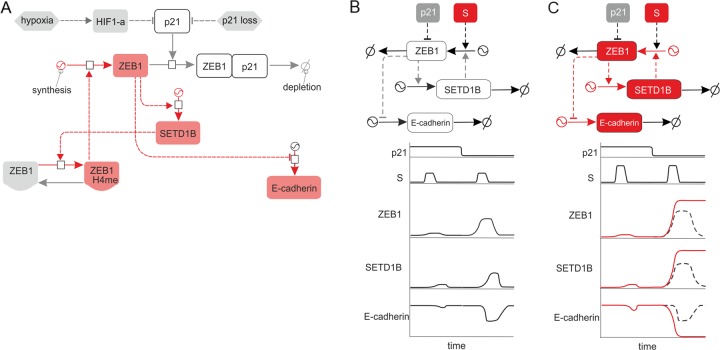
Fig. 6. ZEB1 regulates SETD1B via a regulatory circuit integrated by feedback and feedforward loops.
a This system recapitulates in a regulatory network all the interactions relevant for the interplay between SETD1B and ZEB1 in the context discussed. The key element of the system is the double positive feedback loop between ZEB1 and SETD1B (ZEB1 → SETD1B → ZEB1/H3K4me3 → ZEB1). Through this loop each protein can reinforce the activity/expression of the other. This can amplify the activation of the circuit. b Under low transient stimulation (S) of ZEB1, the circuit responds with transient, low level activation even in the absence of p21. c The structure of the circuit suggests a medium but transient stimulation (S) of ZEB1. This activation can provoke an irreversible enhancement in the expression and activity of both molecules via triggering of SETD1B and feedback-regulating ZEB1 activation. This in turn may trigger the EMT phenotype by consistent, long-lasting inhibition of epithelial marker E-Cadherin. In solid red lines, we represent the long-lasting activation of the circuit, while the black dashed lines represent the transient activation of the circuit that would appear in case of disruption of the positive feedback loop.