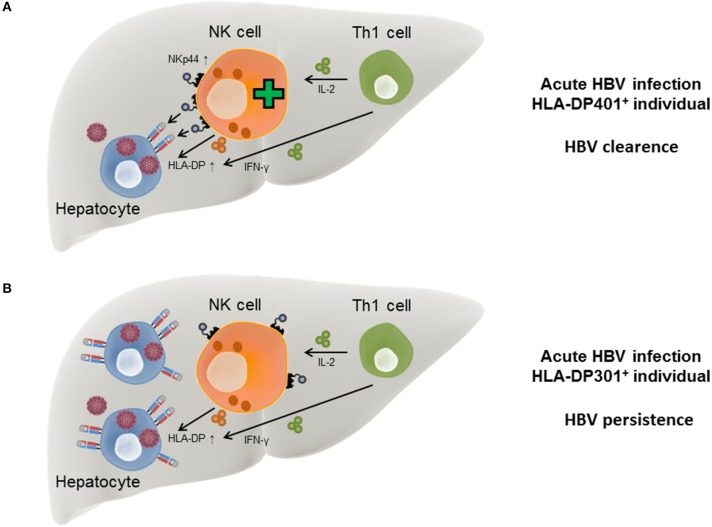
Figure 2.
Model for HLA-DP-NKp44 interactions during HBV infection in individuals with different HLA-DP genotypes. During acute HBV infection HLA-DP molecules are upregulated on the surface of human hepatocytes in response to IFN-γ secreted by Th1 and NK cells. NKp44 expression by NK cells is initiated by IL-2 secreted by Th1 cells. In HLA-DP401+ HBV-infected individuals, NKp44 interacts with HLA-DP401 molecules expressed on the surface of infected hepatocytes, contributing to lysis of infected cells and HBV control (A). In HLA-DP301+ HBV-infected individuals, NKp44 is unable to bind to HLA-DP301 molecules expressed on the surface of infected hepatocytes, resulting in inefficient lysis of infected hepatocytes by innate immune cells and higher risk of chronic HBV infection (B).