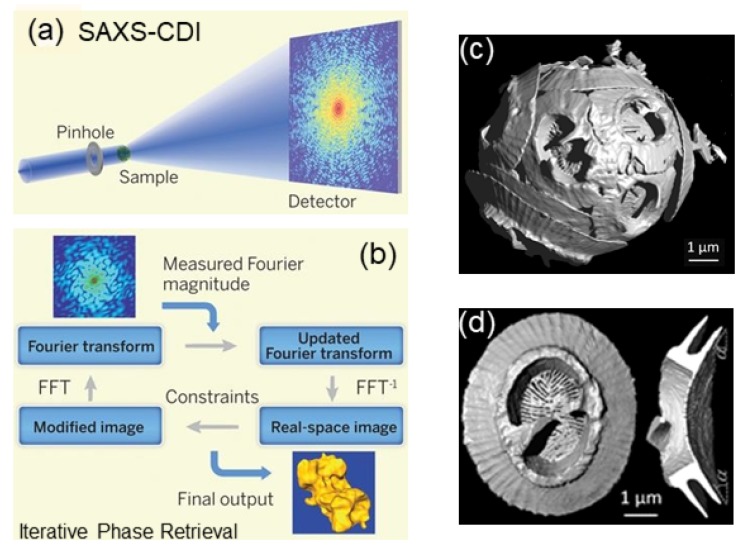
Figure 16.
(a) The optical and detection schemes used in SAXS-CDI. A plane wave illuminates the noncrystalline specimen, and an oversampled speckle pattern is recorded by a high-resolution detector. (b) The phase retrieval procedure involves iterating back and forth between real and reciprocal space. In each iteration, various real space physical constraints such as positive electron density, partially overlapping regions, etc. are imposed, while the measured Fourier amplitude is updated in reciprocal space. Panels (a,b) are adapted from J. Miao et al. [10] with permission from the American Association for the Advancement of Science, ©AAAS 2015. (c) 3D images of coccospheres of G. oceanica RCC1314 reconstructed by tomographic SAXS-CDI. (d) Distal view of the coccolith and a side view along the major axis after sectioning half of the extracted coccolith. Panels (c,d) are adapted from T. Beuvier et al. [142] licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.