Figure 7.
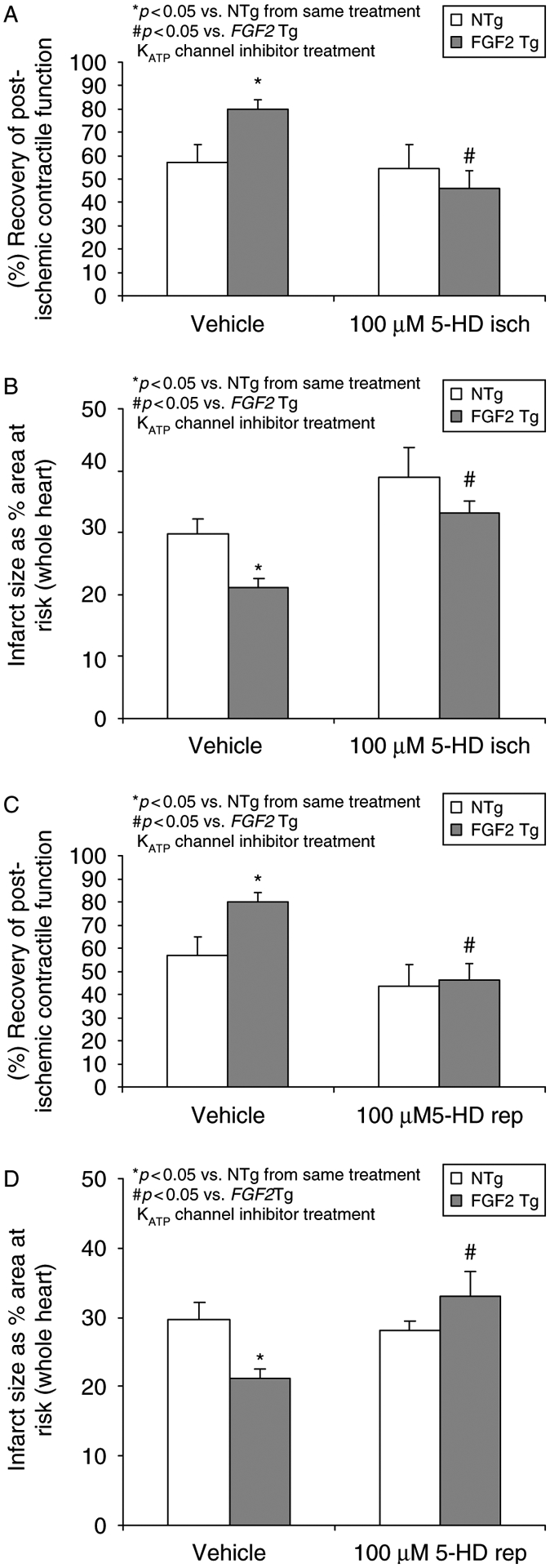
Effects of mitochondrial KATP channels in endogenous FGF2-induced cardioprotection on post-ischemic recovery of contractile function (A and C) and myocardial infarct size (B and D) during ischemia and reperfusion. (Panels A and B) Mouse hearts overexpressing FGF2 (FGF2 Tg) and their wildtype cohort (NTg) were treated with vehicle or the mitochondrial KATP channel inhibitor 5-HD (100 μM) during the last 15 min of baseline equilibration and the first 15 min of ischemia and assessed for the ability to recover contractile function or reduce infarct size following 60 min of low-flow ischemia and 120 min of reperfusion. Inhibition of the mitoKATP channel at ischemia in FGF2 Tg hearts lose cardioprotection against cardiac dysfunction and infarction. (Panels C and D) FGF2 Tg and NTg hearts were treated with vehicle or the mitochondrial KATP channel inhibitor 5-HD (100 μM) during the last 15 min of ischemia and the first 15 min of reperfusion. Similarly, inhibition of the mitoKATP channel at reperfusion blocked FGF2-induced cardioprotection suggesting that this channel is most likely a trigger and an end-effector in this protective phenotype. n = 6–11 hearts per group. *p < 0.05 vs. NTg from same treatment. #p < 0.05 vs. FGF2 Tg KATP channel inhibitor treatment.
