Figure 7.
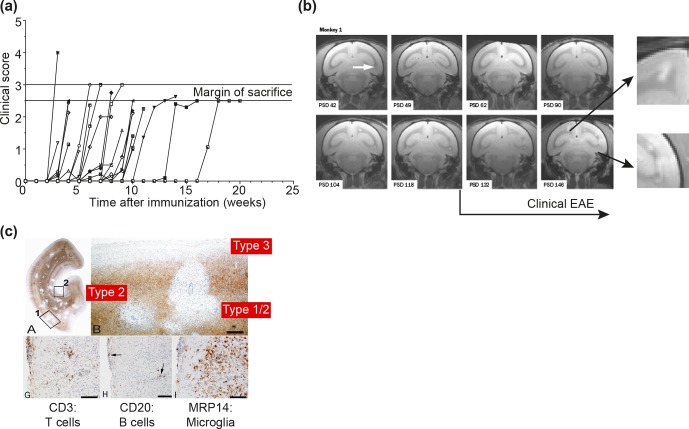
Clinical and pathological aspects of the marmoset EAE model induced with rhMOG/CFA. (a) Depicted is the EAE course in a representative selection of unrelated marmosets receiving a single immunization with rhMOG/CFA on day 0. All monkeys developed clinically evident EAE, but the time of onset varied from 2 to 16 weeks. (b) Serial imaging of a case with late EAE onset, showing early onset of brain lesion formation. The white arrow points to the first detectable lesion. Clearly visible is that formation of new lesions in the depicted brain slice (0.5 mm) is disseminated in time and space. Around the time that clinical signs were diagnosed, lesion colonization of cortical grey matter is detectable (inserted magnifications). (c) PLP staining of a brain hemisphere shows the dramatic demyelination in white and grey matter (a). Different grey matter lesion types identified in the MS brain can be distinguished (b). Lesions are paucicellular with regard to T (CD3) and B (CD20) cells, but contain abundant MRP14 myeloid cells, representing microglia and macrophages.