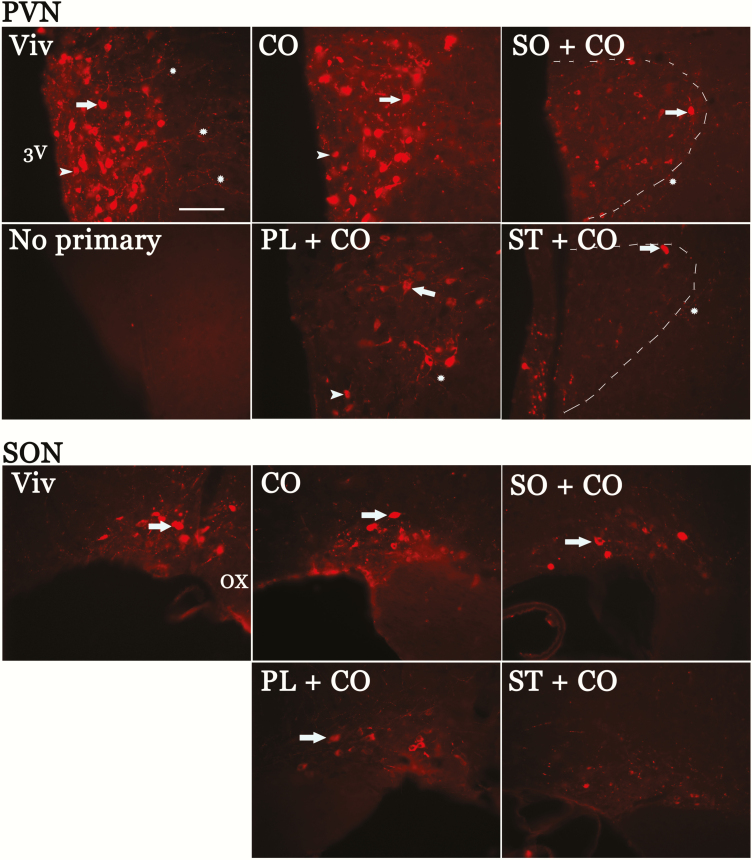
Figure 8.
Dietary soybean oil decreases oxytocin immunoreactivity in the magnocellular neuroendocrine nuclei of the hypothalamus. Oxytocin-neurophysin immunoreactivity in micrographs of hypothalamic tissue sections from perfused brains of male mice fed Viv chow (Viv), CO, SO + CO, PL + CO, or ST + CO diets for 17 to 28 weeks. Reduced immunofluorescence was observed in SO + CO, PL + CO, and ST + CO compared to CO and Viv chow in the large magnocellular neuroendocrine of the SON and PVN and smaller parvocellular neurons of the PVN. 3V, third ventricle; arrow, magnocellular neuroendocrine cells; arrowhead, parvocellular neurons; asterisk, immunolabeled axonal projections; dashed line, PVN boundary in SO + CO and ST + CO; OX, optic chiasm; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; SON, supraoptic nucleus. Calibration bar = 100 μm.