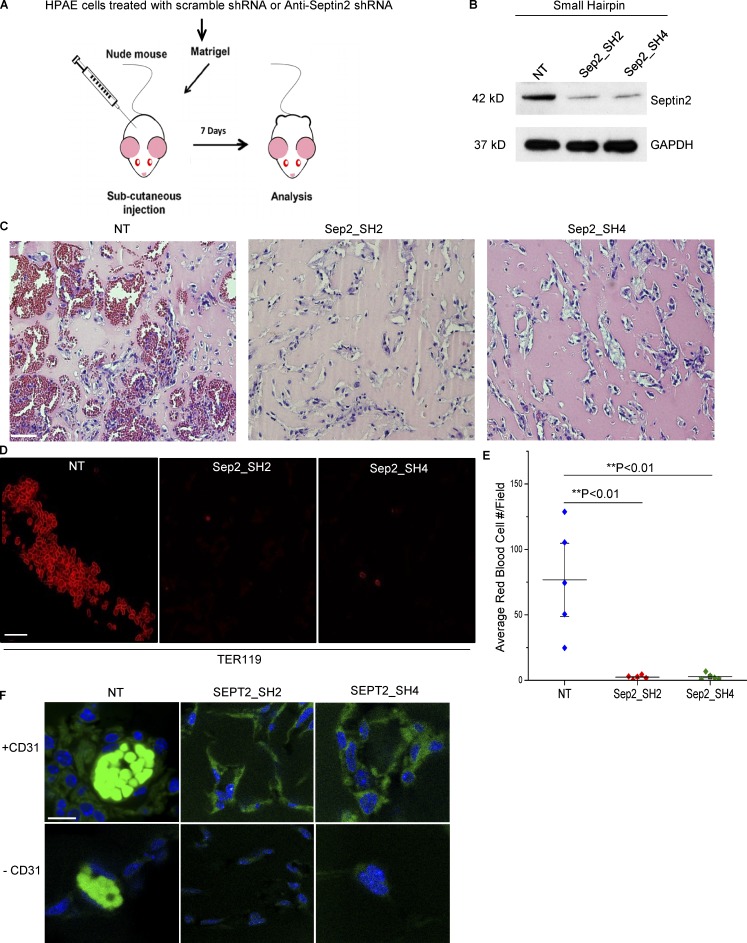
Figure 3.
Septin2 is required for perfused blood vessel formation in vivo. (A) Schematic of the in vivo assay. HPAECs were transduced with lentiviral constructs expressing either control shRNA (NT) or two different shRNAs targeting Septin2 (Sep2-SH2 and Sep2-SH4). Equal numbers of cells from each condition were mixed with Matrigel, subcutaneously injected into athymic nude mice, and harvested 7 d later for analysis of blood vessel formation. (B) Western blot analysis displays downregulation of endogenous Septin2 with respect to GAPDH loading control at time of injection. (C–E) Analysis of Matrigel plugs. Extracted Matrigel plugs were paraffin embedded, and sections were either labeled with hematoxylin and eosin staining to visualize vessel morphology (C; scale bar = 30 mm) or immunostained with antibody targeting mouse erythrocytes (TER119; D; confocal microscopy; scale bar = 20 µm). (E) Average number of red blood cells per field of view were quantified to assess the formation of functionally perfused vessels. Each data point represents the average of four fields of view taken from each of five separate Matrigel plugs per condition and implanted in five separate mice (n = 5). Data are shown as the mean ± SE. Significance was determined using a two-sample t test. (F) Confocal images depicting the presence of HPAECs in Matrigel plug slices from each condition. Slices were stained with DAPI (blue) and human specific anti-CD31 primary antibody (+CD31, green; scale bar = 10 µm). Negative control (−CD31) was performed to reveal nonspecific binding of secondary antibody, and autofluorescence signal (bright green signal in NT samples) is due to autofluorescence of erythrocytes.