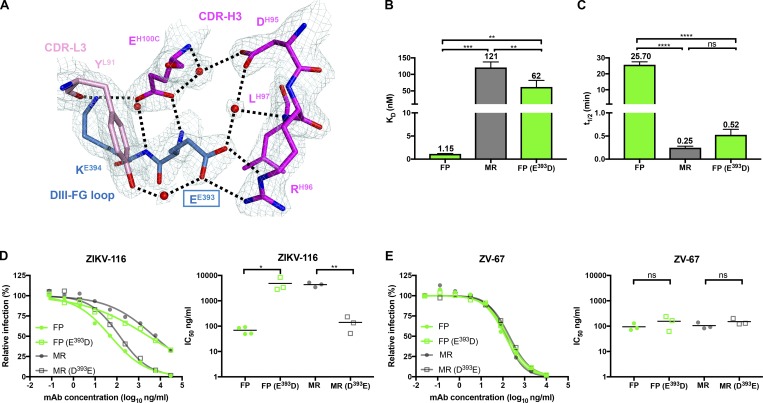
Figure 3.
Variation at residue 393 in the ZIKV-116 epitope is responsible for the neutralization differences between two ZIKV strains. (A) Detailed interactions of DIII residues EE393 and KE394 with ZIKV-116, with 2Fo-Fc electron density map (1.5 σ) colored in pale cyan. The water molecules are shown as spheres and colored in red, and the hydrogen bonds are marked as black dashed lines. (B and C) Comparison of KD and t1/2 of ZIKV-116 to DIII from H/PF/2013 (FP), MR-766 (MR), and FP bearing E393D mutation. The results show the average of at least two independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD. (D and E) Neutralization profiles of mAbs against WT and mutant ZIKV FP and MR RVPs containing reciprocal amino acid substitutions at residue 393 (left). IC50 values from at least three independent experiments performed in duplicate (right). ZV-67 (another ZIKV DIII-LR mAb) served as a control mAb. Serial dilutions of mAbs were incubated with RVPs for 1 h at 37°C, followed by infection of Raji-DCSIGNR cells. GFP-positive, infected cells were determined by flow cytometry at 40 h. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s test (B and C) or two-tailed t tests (D and E). ns, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.