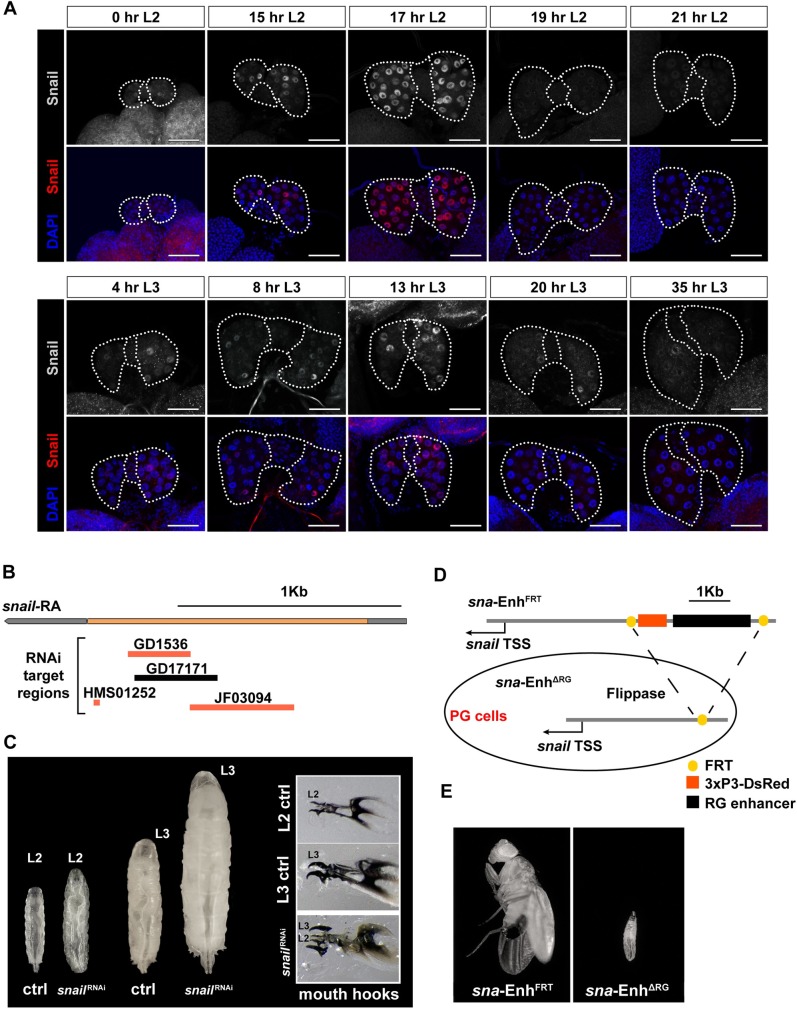
Fig 1. snail is dynamically expressed in the larval PG and required in the PG during development.
(A) Single-plane confocal images showing RGs stained with anti-Snail antibodies and DAPI. w1118 larvae were dissected and examined at various time points during larval stages. The PG and CA are outlined by a white dotted line. Eight to 10 RGs were examined for each condition. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) The Drosophila snail transcription unit and target sequences of existing snail-RNAi lines. Noncoding sequences are in gray, and coding region is in orange. GD1536, GD17171 (from VDRC), HMS01252, and JF03094 (from TRiP) are transgenes that produce dsRNA. (C) PG-specific knockdown of snail caused developmental arrest in L2 and L3 larvae. Control (“ctrl”) L2 were collected at 64 hr AED, whereas snail-RNAi L2 larvae that failed to molt to the L3 stage were collected at 86 hr AED when controls had molted to L3. Control L3 larvae were removed at 92 hr AED, and the arrested snail-RNAi L3 were collected 4 d later when controls had pupariated. Control: UAS-Dicer2; phm22-Gal4>w1118. snailRNAi: UAS-Dicer2; phm22-Gal4>UAS-snail-RNAi (VDRC#50003). (D) Schematic of the sna-EnhFRT allele we used to generate mosaics in which the RG enhancer of snail was deleted (sna-EnhΔRG) because of PG-specific expression of Flippase. (E) Survival of sna-EnhFRT animals and sna-EnhΔRG animals. sna-EnhFRT animals can develop normally to adulthood, whereas sna-EnhΔRG animals arrested development as early L2. AED, after egg deposition; CA, corpus allatum; dsRNA, double-strand RNA; FRT, flippase recognition target; L2, second instar; L3, third instar; PG, prothoracic gland; RG, ring gland; RNAi, RNA interference; TRiP, Transgenic RNAi Resource Project; TSS, transcription start site; VDRC, Vienna Drosophila Resource Center.