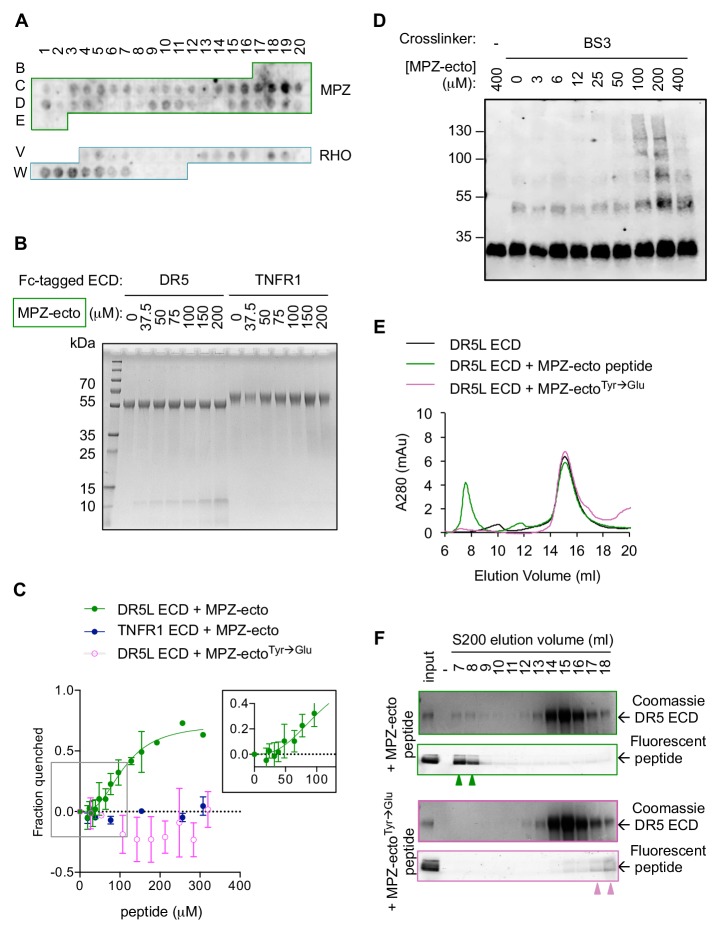
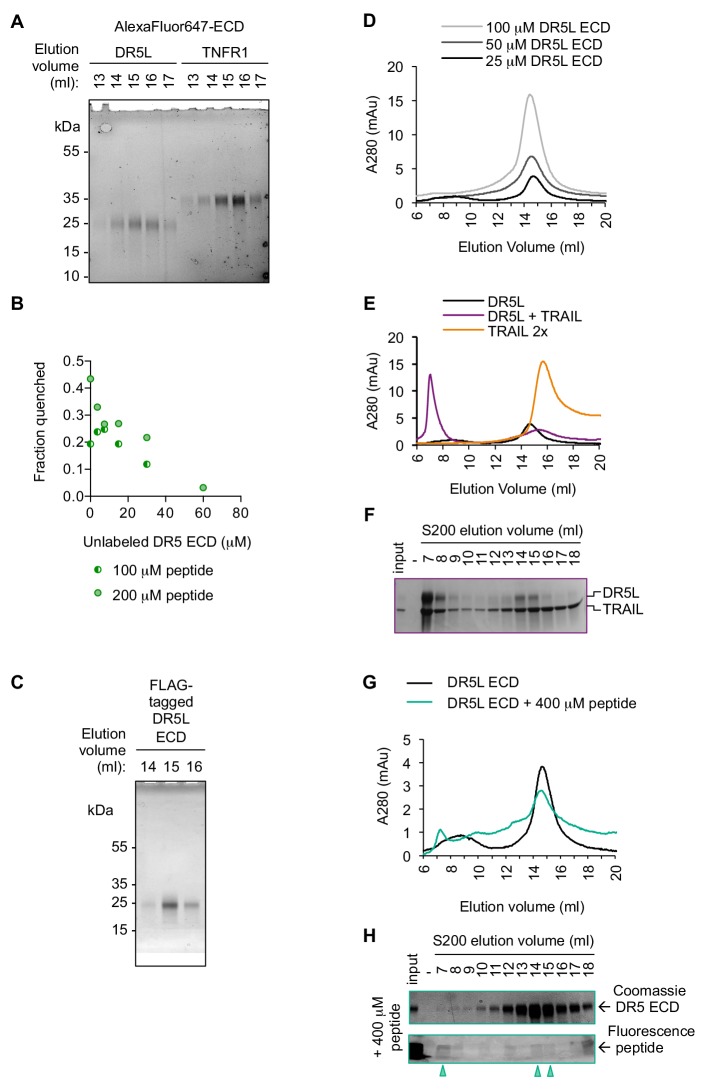
Figure 3. Direct binding of exposed ER-trafficked protein sequences to the DR5 ECD is sufficient to induce oligomerization.
(A) A peptide array tiled with sequences from the ectodomain of myelin protein zero (MPZ) and extracellular loops from rhodopsin (RHO) was incubated with Fc-tagged DR5 ectodomain domain (long isoform, 500 nM). Signal was obtained by probing with anti-Fc. (B) Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel of pulldown on Fc-tagged DR5L ECD (55 kDa) or TNFR1 ECD (65 kDa) incubated with increasing concentrations of the MPZ-ectoVD peptide (apparent MW of 10 kDa, see 'Amino acid sequences of MPZ-derived peptides' for sequence). (C) Fluorescence quenching of AlexaFluor647-DR5L (green) or TNFR1 ECD (blue) was measured with increasing MPZ-ecto peptide to quantify the binding affinity, whereas quenching was not observed with the mutated MPZ-ectoTyr→Glu peptide (magenta) (N = 3, error bars are SD). DR5L ECD binds to the MPZ-ecto peptide with a K1/2 of 109 ± 11 μM with a hill coefficient of 2.6 ± 0.5. (D) SDS-PAGE of recombinant FLAG-tagged DR5L ECD (25 kDa, 10 μM) incubated with MPZ-ecto peptide at the noted concentrations and treated with the amine crosslinker BS3 (100 μM), probed with anti-FLAG. (E) Size exclusion chromatographs of absorbance at 280 nm for 25 μM recombinant DR5L ECD alone (black), pre-incubated with 100 μM fluorescein-conjugated MPZ-ecto peptide (green) or 100 μM fluorescein-conjugated MPZ-ectoTyr→Glu peptide (magenta). (F) SDS-PAGE gels scanned for fluorescence and then stained with Coomassie for eluted size exclusion fractions in (E). Green outlines (top pair) correspond to fractions from DR5L pre-incubated with MPZ-ecto peptide, and magenta outlines (bottom pair) correspond to DR5L with MPZ-ectoTyr→Glu peptide. Lane marked by “-“ denotes a blank lane between the input and 7 ml fraction to minimize spillover of signal from input sample. Arrowheads mark detectable peptide fluorescence in the indicated fractions.
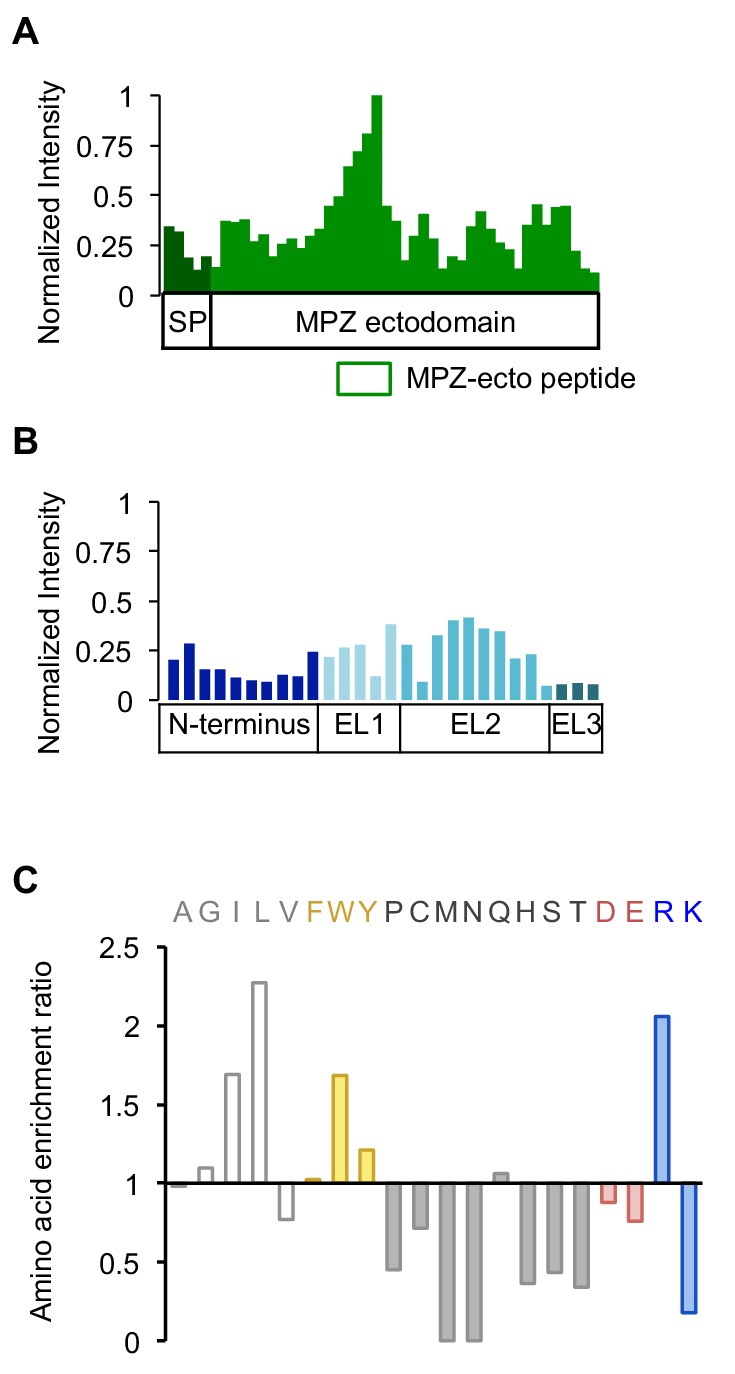
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. DR5 ECD binds to selective subset of sequences displayed by the secretory proteome.