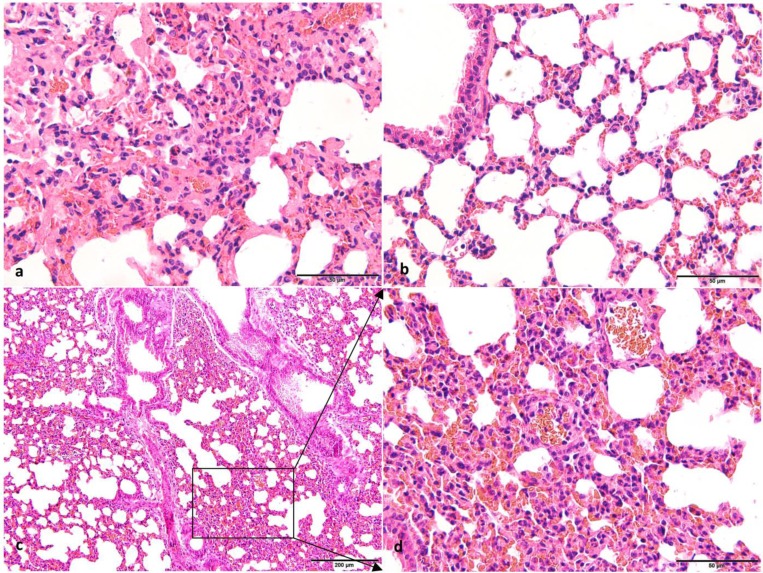
Fig. 3.
Photomicrographs of lung tissues from mice and forest musk deer. (a) The histological structure of the lung of forest musk deer (H&E. 400×, Bar=50 μm). (b) The histological structure of the lung in the control group mice (H&E. 400×, Bar=50 μm). (c) The histological structure of the lung in the test group mice (H&E. 200×, Bar=200 μm). (d) The histological structure of the lung in the test group mice with high-expansion (H&E. 400×, Bar=50 μm). Histopathological observations showed infiltration of numerous erythrocytes, neutrophils, and monocyte in the alveolar lumen of forest musk deer and test group mice. In addition, an area of thickened alveolar wall was observed in the test group mice. There were no histopathological changes in the control group.