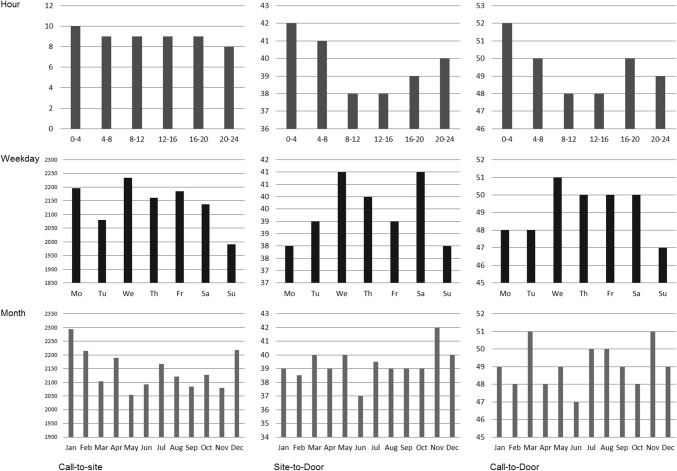
Fig. 1.
Transportation times according to daytime, weekday, and month. Transportation times (minutes) are shown according to hour of the day (clusters of 4 h, upper row); weekday (middle row); and month (bottom row). Left column: patient call to ambulance arrival at site (call-to-site); mid column: ambulance arrival at site-to-door; right column: patient call-to-door. Call-to-site, site-to-door, and call-to-door were prolonged between 00:00 and 04:00 (p < 0.001); the shortest call-to-site, site-to-door, and call-to-door were on Sundays (call-to-site: p = 0.013, site-to-door: p < 0.001, call-to-door: p < 0.001). Month did not significantly impact transportation times (p > 0.05) (note: call-to-site for weekday and month is shown as mean rank (as median minutes are equal for each day and month, i.e., 9 min)