Figure 6.
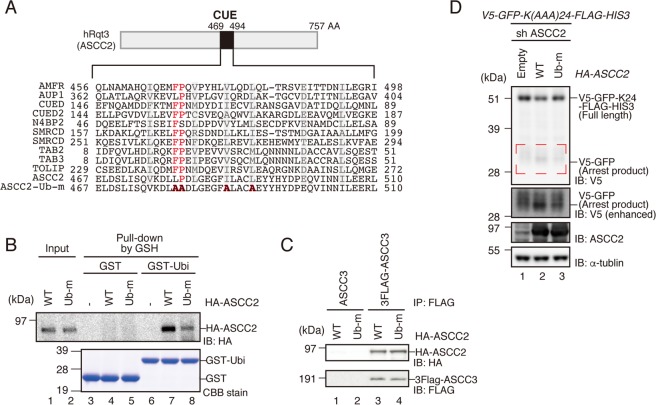
Ubiquitin-binding activity of ASCC2 is crucial for RQC induction. (A) Top: Schematic drawing of the domain structure of ASCC2. Bottom: Amino-acid sequence alignment of conserved residues in CUE domains of the indicated proteins. Mutated residues in Ub-m are shown in bold red. (B) Recombinant HA-ASCC2 or HA-ASCC2-Ub-m mutant (Input), and GST or GST-Ubiquitin were mixed and reacted in vitro, and then pulled down with Glutathione Sepharose. GST-tagged proteins were eluted with glutathione (elution). Both input and elution fractions were analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against HA. Elution fractions were also analyzed by CBB staining. (C) HA-ASCC2 or HA-ASCC2-Ub-m mutant was co-transfected into HEK293T cells along with FLAG-ASCC3, and immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody beads. FLAG-tagged proteins were eluted with FLAG peptides, and the eluted fraction was analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against FLAG and HA. (D) HA-ASCC2 or HA-ASCC2-Ub-m mutant was co-transfected into ASCC2 KD cells along with the V5-GFP-K(AAA)24-FLAG-HIS3 reporter, and protein was analyzed by western blotting with anti-V5 antibodies. Arrest products highlighted by the red dashed line are shown with a longer exposure (V5 enhanced). (B–D) Cropped blots are displayed; full uncropped blots are available in Supplemental Fig. S8. Blots shown are representative of three independent experiments.