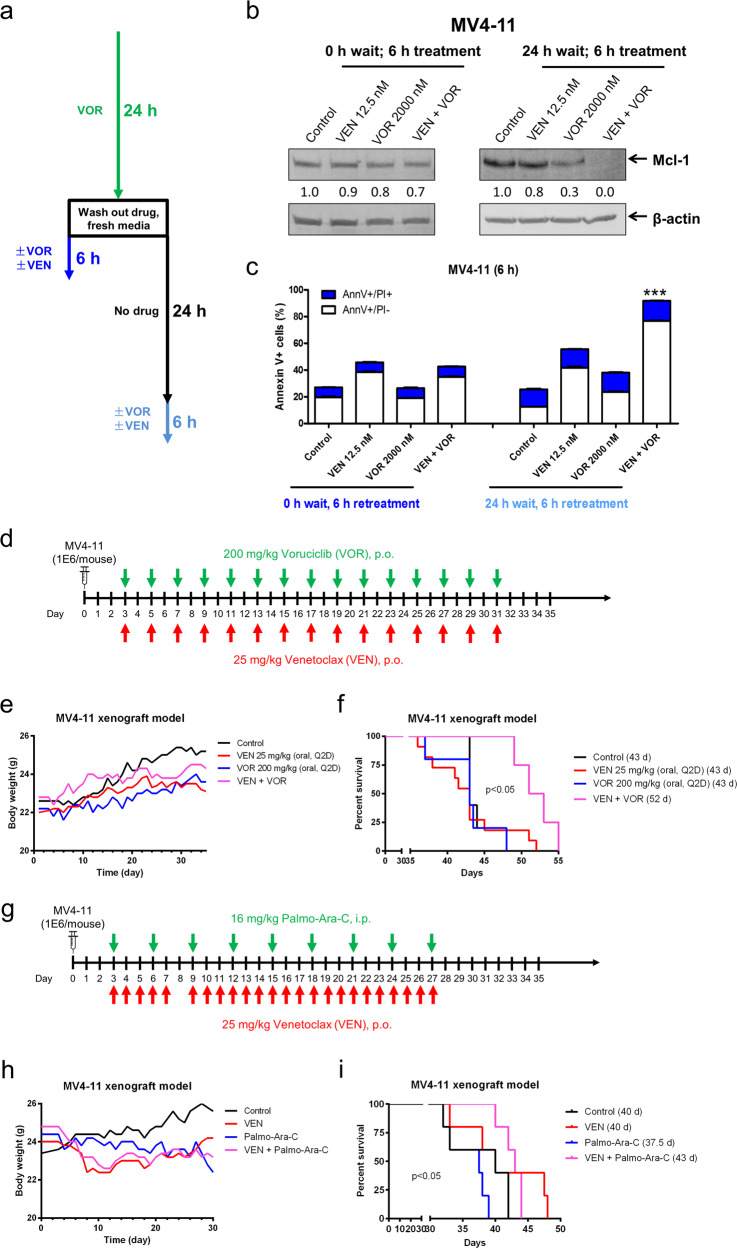
Fig. 5.
Intermittent CDK9 inhibition enhances venetoclax activity in vitro and in vivo. a Schematic for the rechallenge treatments. b, c MV4–11 cells were treated with voruciclib (VOR) for 24 h. The cells were spun and washed with PBS. Cells were cultured in drug-free medium for 0 or 24 h and then treated as indicated for 6 h. Whole-cell lysates from re-treated cells were subjected to western blotting and probed with the indicated antibodies. Relative densitometry measurements were determined using Odyssey Software V3.0 and compared to the control and normalized to β-actin. Re-treated cells were subjected to Annexin V-FITC/PI staining and flow cytometry analyses. ***p < 0.001. d In vivo treatment schema. NSGS mice were injected with 1 × 106 MV4–11 cells via the tail vein and treated Q2D starting on day 3 with 25 mg/kg/inj ABT-199 p.o. and/or 200 mg/kg/inj voruciclib p.o. e Average mouse body weights for the treatment arms were measured on a daily basis. f Kaplan–Meier survival curves for the treatment arms are shown (Mantel–Cox statistical test). g In vivo treatment schema. NSGS mice were injected with 1 × 106 MV4–11 cells via the tail vein and treated starting on day 3 with 25 mg/kg/inj ABT-199 p.o. daily and/or 16 mg/kg/inj palmo-ara-C i.p. Q3D. h Average mouse body weights for the treatment arms were measured on a daily basis. i Kaplan–Meier survival curves for the treatment arms are shown (Mantel–Cox statistical test)