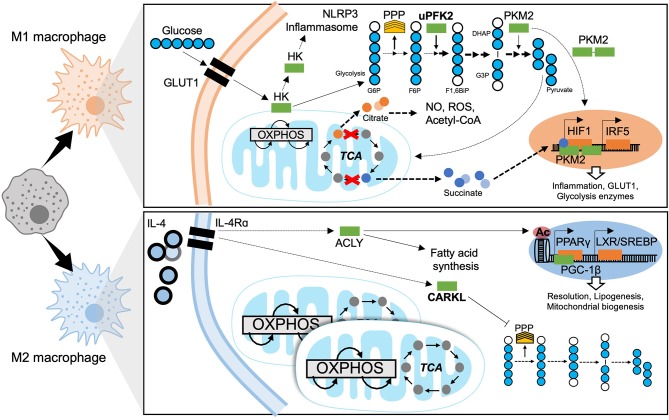
Figure 4.
Metabolic mechanisms of macrophage polarization. M1 macrophages are characterized by predominantly glycolytic metabolism. Glycolysis consists of breaking down a 6-carbon glucose molecule (where each carbon is depicted as a blue circle, white when phosphorylated) into 3-carbon sugars then into pyruvate, ATP, NADH, and H+. The transcriptional programme that supports glycolysis is mediated by HIF1 and at least in part by IRF5. A Glucose substrate is provided by increased expression of the glucose transporter GLUT1. Meanwhile several glycolytic enzymes undertake non-canonical roles to support M1 effector functions. The mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle is disrupted, leading to accumulation of citrate and succinate which also enhance M1 effector function. The M2 macrophage has a fully intact TCA cycle, enhanced OXPHOS and increased mitochondrial biogenesis. ATP citrate lyase (ACLY) is activated downstream of IL4 signaling and enhances M2 effector functions through epigenetic mechanisms and producing substrates for lipogenesis. The sedoheptulose kinase (CARKL) represses the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). Transcriptional programmes for M2 macrophage metabolism are mediated by PPARγ and LXR. GLUT1, Glucose transporter-1; HK, Hexokinase; NLRP3, NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; uPFK2, ubiquitous phosphofructokinase2; PKM2, pyruvate kinase isozyme 2; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; F6P, fructose-6-phosphate; F1,6BiP, Fructose-1,6-biphosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; NO, nitrous oxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species; CoA, Coenzyme A; HIF1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1; IRF5, interferon regulatory factor 5; IL-4, interleukin 4; IL-4Rα, IL-4 receptor alpha; ACLY, ATP-citrate lyase; CARKL, carbohydrate kinase like/sedoheptulose kinase; Ac, acetylation mark; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; LXR, liver X receptor; SREBP, sterol regulatory element binding protein; PGC-1β, PPARγ coactivator 1-beta.