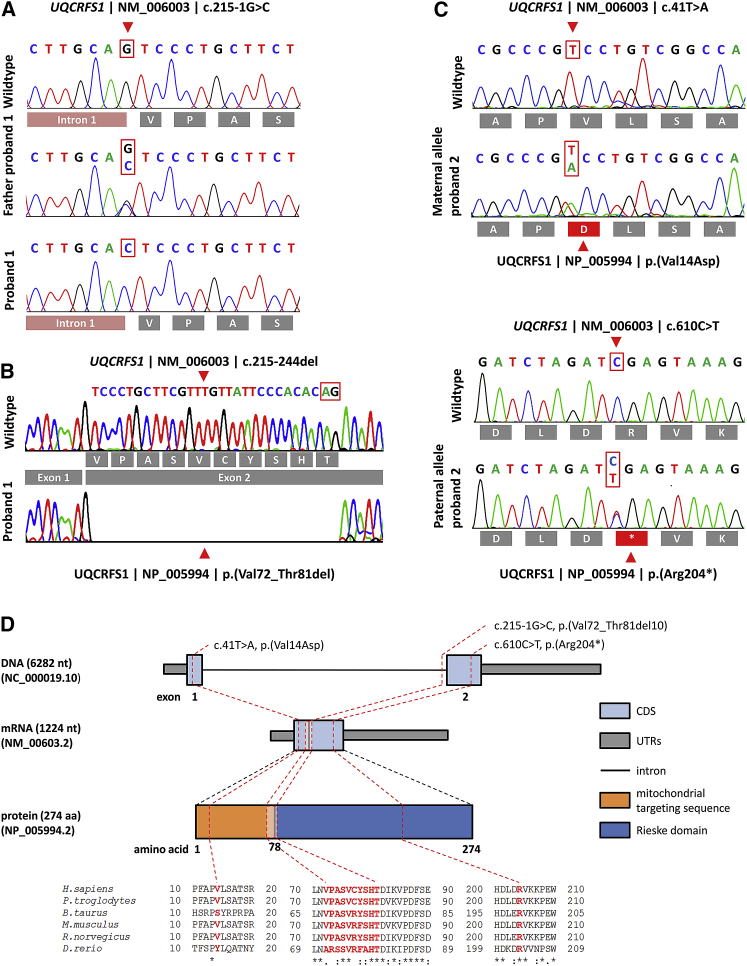
Figure 2.
Molecular Genetic Findings in Both Probands
(A) Electropherograms of the homozygous c.215-1G>C splice-site variant in P1, which was heterozygous in both parents.
(B) Loss of the splice acceptor site of intron 1 leads to activation of an alternative downstream cryptic splice site (highlighted by a red box) with subsequent loss of 30 bp from the cDNA.
(C) Electropherograms of the compound heterozygous variants, c.41T>A inherited from the mother and c.610C>T from the father. The effect of the mutation on the amino acid sequence is depicted below the electropherograms.
(D) Genomic organization of UQCRFS1 into two exons, the mRNA, and the protein structure depicting the location of the identified variants. The localization of the altered amino acids is highlighted on the protein domain structure. Phylogenetic conservation of the affected amino acid residues is presented in the alignment of homologs across different species. Positions of affected amino acids are highlighted in red. NB; the intronic region is not drawn to scale.