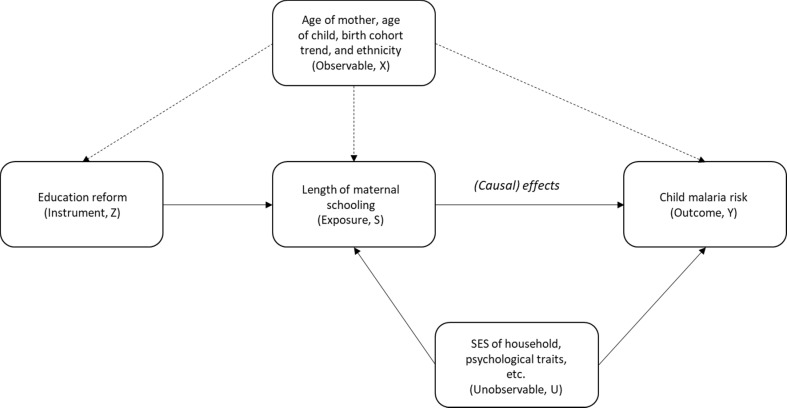
Figure 1.
Causal diagram. This diagram explains the identification assumptions under the two-stage least squares method. I assume that, conditional on X, Z is a valid instrument if 1) Z is strongly correlated with S (relevance), 2) Z is not associated with U and 3) Z affects Y only through its effects on S (exclusion restriction). Under an additional assumption, 4) Z changes S only in one direction (monotonicity), the estimated treatment effects are interpreted as local average treatment effects.