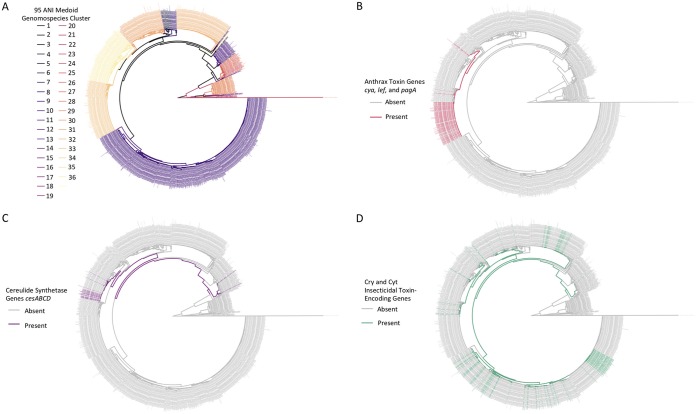
FIG 3.
Maximum likelihood phylogenies of 2,218 B. cereus group genomes with N50 of >20 kbp. Tip and branch labels are colored by genomospecies assignment using medoid genomes of genomospecies clusters formed at the widely used genomospecies threshold of 95 ANI (clusters are arbitrarily numbered) (A) and presence (colored) and absence (gray) of anthrax toxin genes cya, lef, and pagA (B); cereulide synthetase-encoding cesABCD (C); and one or more previously described Cry or Cyt insecticidal toxin-encoding genes (D). Phylogenies were constructed using core SNPs identified in 79 single-copy orthologous gene clusters present in 2,231 B. cereus group genomes. The type strain of “B. manliponensis” (i.e., the most distantly related member of the group) was treated as an outgroup on which each phylogeny was rooted. Virulence genes (cya, lef, and pagA and cesABCD) were detected using BTyper version 2.3.2 (default thresholds), while insecticidal toxin-encoding genes were detected using BtToxin_scanner version 1.0 (default settings; presence and absence of high-confidence, previously known Cry- and Cyt-encoding genes are shown, with predicted putative novel insecticidal toxin-encoding genes excluded).