Figure 1.
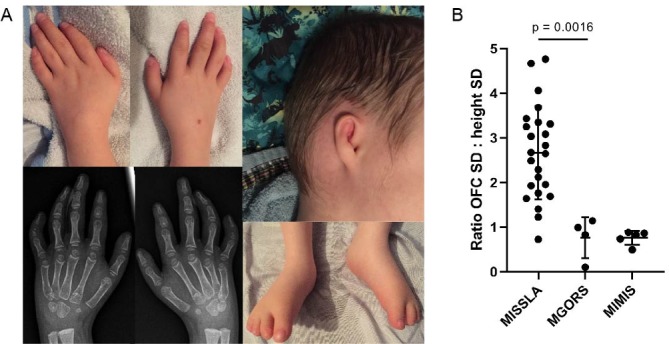
Clinical characteristics of DONSON-MGORS individuals. (A) Photographs of P4 showing tapering fingers, fifth finger clinodactyly caused by hypoplasia of the middle phalanx, small and simply formed ears and shortened toes with oedema evident. (B) Ratio of occupitofrontal circumference (OFC) to height SDs (z-scores) in MISSLA (taken from ref 15), DONSON-MGORS and MIMIS cohorts (taken from ref 17). Note that MISSLA and DONSON-MGORS measurements were taken at the most recent clinical exam, whereas MIMIS were taken at birth. While the most commonly associated syndrome with DONSON variants, MISSLA, shows a skewing of growth parameters due to the extreme disproportionate microcephaly, DONSON-MGORS shows proportionate reduction in size (unpaired t-test, p=0.0016). Separate consent for publication of images was provided by P4. MGORS, Meier-Gorlin syndrome; MIMIS, microcephaly-micromelia syndrome; MISSLA, microcephaly and short stature, with limb anomalies.
