Figure 3. Impact of co-mutations on the microenvironment of KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma.
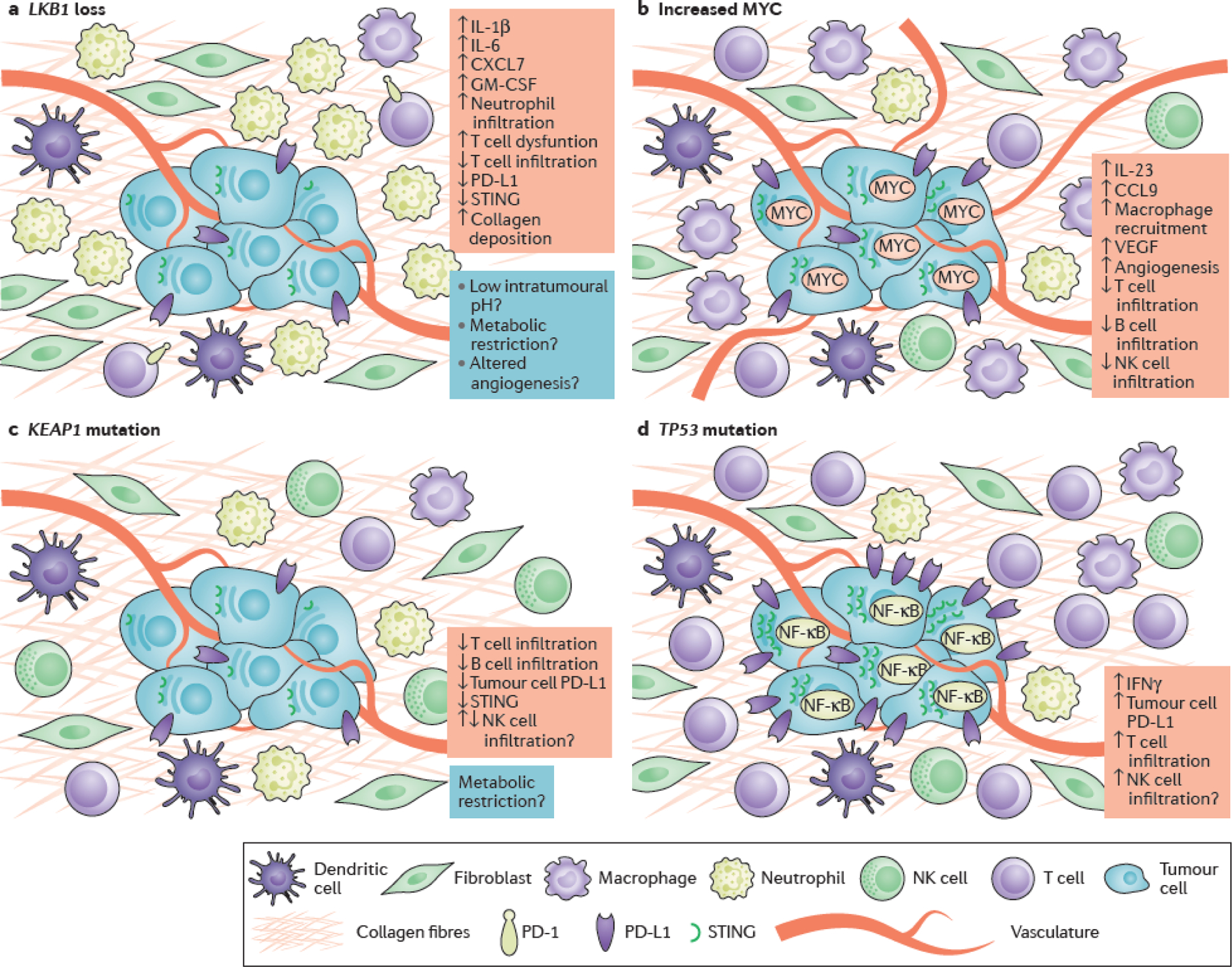
Schematic representation of co-mutation-associated changes in the immune and non-immune microenvironment of KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). (a) LKB1 inactivation promotes epigenetic suppression of STING and insensitivity to cytosolic DNA that accumulates in the cytoplasm of KRAS- and LKB1-mutant (KL) cells due to dysfunctional mitochondria136. KL tumors are further characterized by a pro-inflammatory cytokine milieu with accumulation of immunosuppressive neutrophils, marked paucity of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells and evidence of T-cell exhaustion68, 135. The potential contributions of immune cell metabolic restriction, altered angiogenesis and acidification of the tumor microenvironment (highlighted in blue) to the immune-inert phenotype of KL tumors remain as yet unexplored, but represent plausible directions for future study. (b) MYC fosters immune evasion of murine KrasG12D- driven LUADs through IL-23- mediated expulsion of T, B and NK cells and CCL9-mediated macrophage recruitment and secretion of immunosuppressive VEGF138. (c) KEAP1 mutations, which frequently co-occur with mutations in LKB1, particularly in the context of KRAS-mutant LUAD, have also been associated with low intra-tumoral density of infiltrating T- and B- lymphocytes, although the possible role of KEAP1 loss on NK cell infiltration remains unclear141. Stabilization of NRF2 as a result of KEAP1 inactivation may further promote reduced expression of STING through post-transcriptional regulation142. (d) Finally, somatic TP53 mutations have been shown to mediate NF-κB pathway activation in Kras-mutant murine models of LUAD146. Although TP53 mutations have been associated with reduced production of chemokines required for the recruitment of NK and T cells in some models and human tumors, in the context of KRAS-mutant LUAD TP53 co-alterations promote an inflamed tumor immune microenvironment with increased production of interferon γ (IFNγ) and increased expression of PD-L1 on the surface of tumor cells67, 68, 186.
